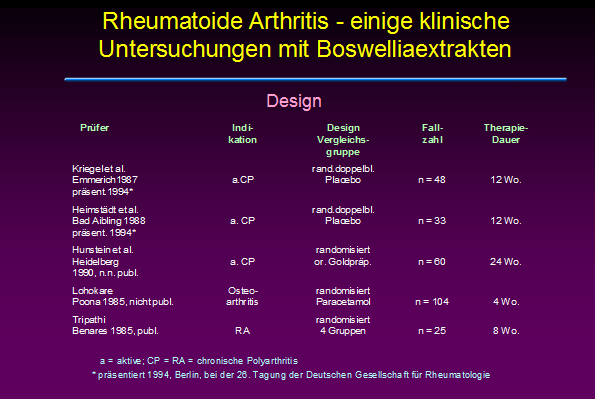
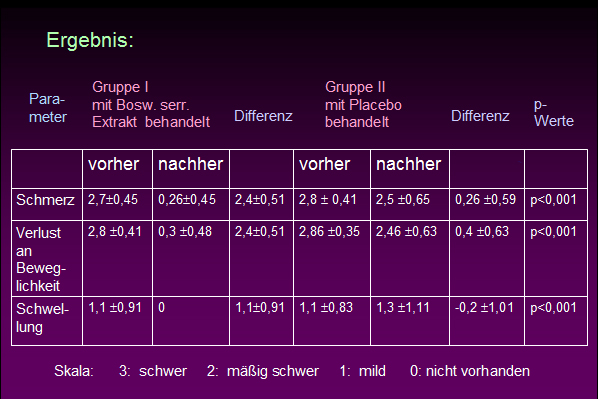
Anfang der 90er Jahre wurden eine Reihe nichtpublizierter Studien vorgestellt, die meist eine Wirksamkeit von Boswelliaextrakten (u.a. H 15 Ayurmedica) bei rheumatoider Arthritis nahe legen:
| 1. |
Biomonitoring the skeletal muscle metabolic dysfunction in knee osteoarthritis in older adults: Is Jumpstart Nutrition® Supplementation effective?
Apurba G, Sudip B
BACKGROUND: This study aimed to investigate the efficacy of Jumpstart Nutrition® dietary supplement (JNDS) for enhancing the skeletal muscle metabolism and function of older adults with knee osteoarthritis (KOA) by evaluating the biomarkers of aberrant levels of serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-10 (IL-10), C-reactive protein (CRP), creatine kinase-muscle (CK-MM), and aldolase-A (Aldo-A).
METHODS: This twelve-week registry included 54 patients treated with JNDS mainly comprised of calcium, phosphorus, vitamin-K, coenzyme-Q, boswellic acid, and curcumin mixed with soy and whey protein (experimental group) and 51 patients treated with symptomatic slow-acting drugs for osteoarthritis (SYSADOA) (control group) for KOA confirmed with radiological images. At week 0 and week 12 for both the groups evaluated, the non-fasting serum levels of TNF-α, IL-10, CRP, CK-MM, and Aldo-A by using appropriate kits.
RESULTS: At week-twelve, the respective values of area under the ROC curves of the studied biomarkers for pooled experimental cohorts were 0.928, 0.907, 0.908, 0.927, and 0.988 having the significance of accuracy (R-square):66.28%, 47.25%, 70.39%, 65.13%, and 68.00%, indicating a satisfactory treatment policy, their mean± SD, and risk ratio, all exhibited highly significant differences (p<0.0001) and KOA-gradation was upgraded between≥2 and ≥3 from≥4 as per the Kellgren-Lawrence scale compared to the control. Fewer patients had to use emergency medications (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS: Results suggest that JNDS may be effectively used to strengthen the skeletal muscle metabolism and function of elderly patients with KOA confirmed with the stabilization of studied biomarkers as an alternative to the treatment of SYSAD correlated with ROC curves and the Kellgren-Lawrence scale.
Caspian J Intern Med. 2023;14(4):590-606.
PMID: 38024172 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 2. |
Extracts Ameliorates Symptom of Irregularities in Articular Cartilage through Inhibition of Matrix Metalloproteinases Activation and Apoptosis in Monosodium-Iodoacetate-Induced Osteoarthritic Rat Models.
Kim J, Eun S, Jung H, Kim J, Kim J
The research examined the effects of extracts (BSE) on a rat model of osteoarthritis induced by monosodium iodoacetate (MIA). The severity and progression of MIA-induced osteoarthritis were assessed using microcomputed tomography imaging. Additionally, the study investigated the impact of BSE various the biomarkers associated with osteoarthritis, including anabolic and catabolic factors, pro-inflammatory factors, and apoptosis factors. The evaluation methods employed included western blot, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis in osteoarthritic rats. Supplementing osteoarthritic rats with BSE reduced tissue injury, cartilage destruction, and decreased in MIA-induced roughness on the articular cartilage surface. MIA-treated rats exhibited increased expressions of phosphorylation of Smad3, MMPs, p-IκB, p-NF-κB, and pro-inflammatory factors (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and COX-2), which were mitigated by BSE supplementation. Furthermore, protein expressions related to apoptosis pathways were significantly reduced in MIA-induced rats supplemented with BSE. These findings suggested that BSE ingestion may enhance the inflammatory response, decrease JNK-dependent MMPs activation, and alleviate caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in MIA-induced osteoarthritic rat models. Consequently, BSE exhibits potential as a therapeutic agent for treating osteoarthritis.
Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2023 Sep;28(3):285-292.
PMID: 37842260 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 3. |
Efficacy of Herbal Medicine in Hand Osteoarthritis: A Narrative Review.
Aghili SM, Sahebari M, Salari M, Noorabadi P
OBJECTIVE: Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the most prevalent joint disorders in the world that has placed an enormous economic and social burden on governments and healthcare sectors in many countries. Hand OA (HOA) is the most common peripheral arthritis, which is less investigated than knee and hip OA. Due to limited approved drug choices and adverse effects of long-term use of current regimens, we aimed to review the existing evidence that were used as oral herbal medicine to treat HOA.
METHODS: The PubMed database was searched for both observational and interventional studies that have investigated herbal medicine safety and efficacy in HOA, written in English and published between 2010 and 2022.
RESULTS: A total of 5 original articles fulfilled the inclusion criteria, and each article assessed a different herbal regimen. Overall, it seems desirable to add specific herbal treatments to the regimen of HOA patients, specifically in case of early stages of HOA.
CONCLUSION: Currently, the need for a low-risk alternative treatment in HOA patients is felt more than ever. There are reliable references relating to the safety of Korean red ginseng, GCSB-5, XLGB, and GS-GCu in these patients, although their efficacy was limited. Additionally, herbs like curcumin and have positively affected patients with knee osteoarthritis. However, there is a lack of strong evidence supporting their effectiveness in hand osteoarthritis (HOA). This emphasizes the potential benefits that these herbs may have for HOA patients.
Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2024;20(1):39-45.
PMID: 37691222 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 4. |
Efficacy of Extract and/or an Omega-3-Based Product for Improving Pain and Function in People Older Than 40 Years with Persistent Knee Pain: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Clinical Trial.
Pérez-Piñero S, Muñoz-Carrillo JC, Victoria-Montesinos D, García-Muñoz AM, Andreu-Caravaca L, Gómez M, Schölzel M, García-Guillén AI, López-Román FJ
A single-center, randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial with four arms was conducted in healthy subjects with persistent knee discomfort (pain intensity on 1-10 cm visual analog scale (VAS) > 3) aged 40 years and older treated with a dietary supplement for 8 weeks. The study groups were extract ( = 29), an omega-3-based product (AvailOm 50 High EPA) ( = 31), + AvailOm ( = 30), and placebo ( = 30). The intake of + AvailOm improved the quality of life (QoL) (WOMAC index) and some variables of muscle strength. Statistically significant differences between the AvailOm and the placebo groups in the decrease of pain intensity were found. Weekly VAS scores showed a significant decrease in pain perception when comparing the AvailOm product to the placebo, with the lowest VAS scores at week 8. Consumption of improved sleep latency. The time to perform the Up and Go test decreased after the intake of AvailOm. There was an increase in the omega-3 fatty acids, with the greatest increase in the + AvailOm group. AvailOm was safe and effective in reducing pain and improving the QoL and functionality of subjects over 40 years with persistent knee pain.
Nutrients. 2023 Sep;15(17):.
PMID: 37686880 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 5. |
Efficacy of a proprietary combination of seeds and rhizome extracts in osteoarthritis: a clinical investigation.
Prasad N, Vinay V, Srivastava A
BACKGROUND: NXT15906F6 (TamaFlex™) is a proprietary blend containing standardized seeds and rhizome extracts. Earlier, NXT15906F6 supplementation demonstrated reduced knee joint pain and improved musculoskeletal functions in healthy and knee osteoarthritis (KOA) subjects.
OBJECTIVE: The present randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was focused on validating the clinical efficacy of NXT15906F6 in a larger number of subjects with KOA.
METHODS: Male and female subjects (age: 40-70 years; body mass index [BMI]: 20-29 kg/m] were randomized into three groups receiving placebo ( = 50), NXT15906F6 ( = 50) or a blend of and extracts (CLBS) ( = 50). Subjects consumed 250 mg NXT15906F6, 1,000 mg CLBS or a matched placebo daily after breakfast over a period of 30 consecutive days. The primary efficacy outcome was the improvement in total Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) scores, and the secondary efficacy measures included various tests on joint pain and musculoskeletal functions and evaluations ofserum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and a cartilage degradation marker, C-terminal telopeptide of type II collagen in urine (uCTX-II).
RESULTS: NXT15906F6 significantly ( < 0.001) reduced the WOMAC scores and improved musculoskeletal function scores in the participants as compared with baseline and placebo. NXT15906F6 participants reduced knee pain and improved musculoskeletal functions as early as day 5 of supplementation. In contrast, CLBS supplementation failed to show early efficacies in pain and functional scores, except for 30s-CST and primary knee flexion. The NXT1506F6-supplemented participants significantly reduced serum hs-CRP and uCTX-II levels from baseline and as compared with the placebo. Both supplementations did not alter the subjects' clinical chemistry, hematology, and vital parameters.
CONCLUSION: The anti-inflammatory botanical composition NXT15906F6 supplementation mitigated joint pain and improved musculoskeletal functions and joint motility in KOA subjects. This botanical composition was also well-tolerated by the volunteers.
Food Nutr Res. 2023;67():.
PMID: 37351019 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 6. |
A Retrospective Observational Study Evaluating the Synergistic Effect of a Novel Combination of Alfapin + Native Type 2 Collagen + Mobilee (Hyaluronic Acid) + CurQlife (Curcumin) Nutraceuticals in the Symptomatic Improvement of Knee Osteoarthritis.
Kamat YD, Das B, Thakkar K, Mahajan M
Background Treatment of pain and inflammation form the mainstay of osteoarthritis (OA) management. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), due to their inflammation-blocking mechanism, are a highly effective class of drugs for chronic pain and inflammation in OA. However, this comes at a cost of increased risk for multiple adverse effects, including gastrointestinal bleeding, cardiovascular side effects, and NSAID-induced nephrotoxicity. To minimize the potential risk of an adverse event, numerous regulatory bodies and medical societies recommend using the lowest effective NSAID dose for the shortest time necessary. One potential strategy to achieve this is the use of disease-modifying osteoarthritis drugs (DMOADs) containing anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties instead of NSAIDs for the management of OA. This study focuses on the efficacy of Clagen™ [Aflapin ( extract) + native type 2 collagen + Mobilee (hyaluronic acid (60-70%), polysaccharides (>10%), and collagen (>5%)) + CurQlife (Curcumin)] for the symptomatic improvement in OA patients as well as if this combination is effective in the long-term management of OA instead of NSAIDs. Methodology In this retrospective observational study, a total of 300 patients were screened, of whom 100 OA patients who fulfilled the criteria and agreed to be part of the study were enrolled. The data were analyzed to evaluate the efficacy of the nutraceutical formulation Clagen™ in patients with OA of the knee. From the baseline to two months, primary outcomes of improvement in the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) score, range of motion, and Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) were measured at monthly follow-up. Statistical analyses were performed according to the results obtained from the parameters. The tests were performed at a 5% significance level (p <0.05). The qualitative characteristics were described using absolute and relative frequencies, and the quantitative measures were described as summary measures (mean, standard deviation). Results Of the 100 patients enrolled in the study, 99 (64 males and 35 females) completed the study. The mean age of the patients was 50.6 ± 13.9 years, and the mean body mass index was 24.5 ± 3.5 kg/m. The statistical analysis of the outcomes from the baseline to the two-month follow-up was analyzed using paired t-test. The difference in the mean of VAS pain score at baseline and two months was 3.3 ± 1.8 [t (97) = 18.2; p < 0.05], which showed a significant reduction in pain at two months. Moreover, the difference in the mean of the goniometer value of 7.3 ± 7.3 [t (98) = -10.0, p < 0.05] indicated statistically significant improvements in the range of motion. It was also observed that Clagen™ significantly improved the composite KOOS score by 10.8% at the end of two months. Similarly, KOOS scores for Symptoms, Function, and Quality of Life showed improvements of 9.6%, 9.8%, and 7.8%, respectively, and were statistically significant (p < 0.05). Conclusions Clagen™ exerted positive adjuvant effects in the management of OA. The combination not only improved the symptoms and quality of life but, in the light of future perspective, NSAIDs can be withdrawn in OA patients, considering their long-term negative effects. To validate these findings further long-term studies with a comparison arm of NSAIDs are needed.
Cureus. 2023 Mar;15(3):e36123.
PMID: 37065333 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 7. |
Evaluation of the effectiveness of topical oily solution containing frankincense extract in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.
Mohsenzadeh A, Karimifar M, Soltani R, Hajhashemi V
OBJECTIVE: Pharmacological treatments of osteoarthritis (OA) have several side effects. Boswellia serrata resin (frankincense) is rich in boswellic acids that have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects; though, their oral bioavailability is low. The aim of this study was evaluation of the clinical effectiveness of frankincense extract in the treatment of knee OA. In a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial, eligible patients with knee OA were randomly divided into two groups of drug (33 patients) and control (37 patients), to use oily solution of frankincense extract or placebo, respectively, on the involved knee three times daily for four weeks. WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index), VAS (visual analogue scale; for pain severity), and PGA (patient global assessment) scores were determined before and after intervention.
RESULTS: For all evaluated outcome variables, there was a significant decrease from baseline in both groups (P < 0.001 for all). Furthermore, the end-of-intervention values for all parameters were significantly lower in drug group than placebo group (P < 0.001 for all), showing more effectiveness of drug compared to placebo.
CONCLUSION: Topical oily solution containing enriched extract of boswellic acids could decrease pain severity and improve the function in patients with knee OA. Trial Registration Trial registration number: IRCT20150721023282N14. Trial registration date: September 20, 2020. The study was retrospectively registered in Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (IRCT).
BMC Res Notes. 2023 Mar;16(1):28.
PMID: 36869332 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 8. |
and extract combination for hand osteoarthritis: an open-label pre-post trial.
Henrotin Y, Dierckxsens Y, Delisse G, Maes N, Albert A
CONTEXT: Osteoarthritis (OA) of the hand is a common painful musculoskeletal disorder with no cure. There is a need for an efficient and safe treatment to relieve OA pain.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the effects of a and food supplement in addition to standard care on hand pain.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: This open-label, non-controlled, post-observational study was based on 232 patients suffering from hand pain with or without joint deformity. Patients received a medical prescription for a three-month treatment with a food supplement containing 89 mg of dry extract, 120 mg of resin, and 1.8 µg vitamin D. Pain was evaluated on a 10-point visual analog scale (VAS). The number of painful hand joints, patient satisfaction, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs intake, and side effects were also recorded.
RESULTS: Baseline pain intensity (regression coefficient ± : -0.19 ± 0.01, < 0.0001) and the number of painful joints (regression coefficient ± : -0.022 ± 0.0029, < 0.0001) decreased significantly throughout the 3 months treatment period. NSAIDs intake and topical drug application were significantly decreased by 64% ( < 0.0001) and 79% ( < 0.0001) after 12 weeks, respectively. Only 3/239 (1.3%) patients reported side effects probably related to the product. 80.3% were satisfied with the treatment and 75.5% wished to continue treatment.
CONCLUSION: This is the first clinical trial showing that and resin can relieve symptoms in patients with hand osteoarthritis. The study provides useful information for the design of a clinical trial including a broader population.
Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):2295-2299.
PMID: 36416059 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 9. |
Long-term effects of a diet supplement containing oil and in dogs with osteoarthritis following physiotherapy treatments: a randomised, placebo-controlled and double-blind clinical trial.
Gabriele V, Bisanzio D, Riva A, Meineri G, Adami R, Martello E
Dogs are commonly affected by Osteoarthritis (OA). Different approaches can be used to alleviate animals' symptoms. In this randomised, placebo-controlled and double-blind clinical trial, we performed a three months follow-up study assessing the efficacy of a food supplement containing natural ingredients ( oil, Roxb. Phytosome and Zingiber officinale extract) in dogs with OA after the interruption of physiotherapy that was performed during the previous three months. Inflammation and oxidative stress were reduced in the treated group (higher glutathione (GSH) and lower C-reactive protein [CRP] levels in blood) as well as chronic pain.
Nat Prod Res. 2023 Jun;37(11):1782-1786.
PMID: 36067506 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 10. |
[Complex effects of physical exertion with dietary supplements Cartilox in pain syndrome effectiveness and safety evaluation].
Shavlovskaya OA
UNLABELLED: A promising direction of osteoarthritis (OA) therapy is currently being considered pharmaceutical compositions of Symptomatic Slow Acting Drugs for Osteoarthritis (SYSADOA), which include type II collagen. A clinical observational study was conducted.
OBJECTIVE: To Identify the effect of physical activity complex effects with dietary supplements Cartilox (composition: hydrolyzed type II collagen, hyaluronic acid, boswellia, curcumin, piperine) on the severity of pain syndrome in OA knee and hip joint patients, low back pain (LBP); assessment of the need for the appointment of NSAIDs against the background of taking Cartilox.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: The study included 60 patients aged 35-65 years, with a confirmed diagnosis of knee and hip OA I-II st., LBP with a slight degree of severity of pain syndrome - 4-5 points on a numerical rating scale (NRS). Patients with comorbid diseases: arterial hypertension (AH), type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM-2), hypothyroidism, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract). By randomization, the patients were divided into two groups: Main group (n=30; 54.36±8.57 years) received a complex effect of non-drug therapy (physical therapy complex) with dietary supplements Cartilox 1 sachet per day during or immediately after meals for 1 month, in combination with non-medical therapy (physical therapy complex). And Control group (n=30; 53.03±16.18 years) used only non-medical therapy (physical therapy complex). In both groups, topical NSAIDs were used «on demand». The patients included in the study had imaging data of the spine and joints. Clinical and neurological examination was used: day 0 (Visit 1), Day 14 (Visit 2), Day 30 (Visit 3) of therapy. The dynamics of the condition was assessed: 10-point NRS of pain assessment (at rest, while walking, palpation), functional status of Oswestry Disability Index (ODI), blood pressure (BP) was measured, the dynamics of biochemical parameters (before and after 30 days) of blood glucose, liver enzymes (AST, ALT), weight indicators, registration of adverse events (AEs). A sub-objective assessment (1 to 5 balls) was given to the patient and the physician.
RESULTS: Against the background of taking Cartilox, a statistically significant decrease in the severity of pain syndrome was noted, an improvement on ODI (to a greater extent in the Main group vs the Control group). In no case has a registered AEs. Changes in the level of biochemical blood parameters (glucose, liver enzymes) and blood pressure levels were not observed. The topical NSAIDs use was observed only in the Control group.
CONCLUSION: The complex effect of physical exertion with dietary supplements Cartilox can be recommended for patients with unexpressed pain syndrome (4-5 points on the NRS) with LBP and knee and hip OA (I-II st.). The absence of changes in the level of biochemical parameters of blood and blood pressure makes it possible to recommend Cartilox to patients with OA and comorbid diseases.
Vopr Kurortol Fizioter Lech Fiz Kult. 2022;99(4):20-28.
PMID: 35981338 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 11. |
Use of an alfa-lipoic, Methylsulfonylmethane, Boswellia serrata and Bromelain dietary supplement (OPERA®) for aromatase inhibitors-related arthralgia management (AIA): a prospective phase II trial (NCT04161833).
Desideri I, Lucidi S, Francolini G, Meattini I, Ciccone LP, Salvestrini V, Valzano M, Morelli I, Angelini L, Scotti V, Bonomo P, Greto D, Terziani F, Becherini C, Visani L, Livi L
Aromatase Inhibitors (AIs) are recommended for the adjuvant treatment of hormone receptor positive breast cancer in both high-risk pre-menopausal and post-menopausal population; arthralgia is the main cause of discontinuation of therapy and affects up to 25% of population on AI treatment. The objective of the study was to prospectively evaluate OPERA® (GAMFARMA srl, Milan, Italy), a new dietary supplement where α-Lipoic acid, Boswellia serrata, Methylsulfonylmethane and Bromelain are combined in a single hard-gelatin capsule to be taken once a day. Fifty-three patients with arthralgia (NCI-CTCAE v4.0 grade ≥ 1) occurring during AI therapy were enrolled. All patients received OPERA® from enrollment (T0) up to sixth months (T3). Patients' AI-related arthralgia was evaluated every two months with VAS Scale, PRAI questionnaire, and CTCAE scale. Primary endpoint was the number of patients with symptom resolution (G0) at T3 if compared to T0, according to CTCAE and VAS scale. Secondary endpoints were decrease in arthralgia intensity measured with PRAI score at T3 compared to baseline, safety of OPERA® and rate of AI interruption. Treatment with OPERA® supplement was overall well tolerated; no relevant toxicities related to OPERA® intake were reported. Seven subjects (13.2%) were not included in the final analysis because of consent withdrawal. 46 participants were eligible for final analysis. According to CTCAE scale, 10 out of 46 patients reported symptoms resolution at 6-month follow-up from the time of enrollment T0 (p = 0.0009). According to VAS score, 5 patients reported complete resolution of symptoms at T3 if compared to baseline starting situation T0 (p = 0.0222). Analysis of PRAI score showed a significant reduction in arthralgia-related pain perceived (p = 0.0001). OPERA® was able to reduce the intensity of arthralgia related to AI therapy. Randomized, double-blind studies are warranted to confirm the effectiveness of this dietary supplement.
Med Oncol. 2022 Jun;39(8):113.
PMID: 35666314 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 12. |
Efficacy and Safety of Aflapin®, a Novel Extract, in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Short-Term 30-Day Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study.
Karlapudi V, Sunkara KB, Konda PR, Sarma KV, Rokkam MP
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVE: Aflapin, also known as AprèsFlex was developed as an enhanced bioavailable extract of gum resin, standardized to 20% 3-O-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid. This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial confirms the efficacy of Aflapin in ameliorating the symptoms of osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee.
METHODS: Based on the inclusion/exclusion criteria of the American College of Rheumatology, seventy subjects were recruited and randomized into Placebo (n = 35) and Aflapin (n = 35) groups. Subjects received either 100 mg Aflapin or a placebo for 30 days. All subjects were evaluated for pain and physical function using the standard tools i.e., Visual Analog Scale (VAS), Lequesne Functional Index (LFI), and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) at the baseline (Day 0), 5, and 30 days of treatment. Additionally, several inflammatory and cartilage biomarkers, including matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), high-sensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP), Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein (COMP), and collagen type II cleavage (C2C) were evaluated. Total blood chemistry analyses were conducted to affirm the safety of Aflapin.
RESULTS: Sixty-seven subjects completed the study. Aflapin conferred significant improvements in pain scores as early as five days of treatment. Post-trial, VAS, LFI, WOMAC pain, WOMAC stiffness, WOMAC function, and total WOMAC scores decreased in the Aflapin group by 45%, 40.9%, 44.4%, 66.3%, 44.4%, and 48%, respectively. Aflapin supplementation also reduced circulating MMP-3, TNFα, hsCRP, and C2C.
CONCLUSION: This investigation affirms that Aflapin is clinically efficacious, fast-acting, and safe in the management of osteoarthritis. No significant adverse effects were observed.
J Am Nutr Assoc. 2023 Feb;42(2):159-168.
PMID: 35512759 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 13. |
Ingredients of a Natural Oral Nutritional Supplement and Their Role in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis.
Bharat KT, Manhas NS, Gutcho J, Lin J, Bhattacharyya S, Kounang R
Osteoarthritis is a prevalent degenerative disease affecting a large portion of the world's aging population. Currently, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and acetaminophen are first-line medications for treating osteoarthritis patients' pain. However, several studies have noted that while these medications control pain they do not halt progressive degeneration and tend to have an unfavorable side-effect profile with prolonged use. Recently, due to their more favorable side-effect profiles, herbal alternatives for controlling osteoarthritis symptoms and for alleviating the progression of the disease are being increasingly studied. Synogesic is a newly developed herbal supplement blend by renowned orthopedic surgeons and physiatrists consisting of turmeric, rutin, ginger root, vitamin C, vitamin D, and boswellia extracts. A study by Sharkey et al. has commented on the efficacy of the blend on the patients with knee osteoarthritis. So far, a review on the ingredients of the blend has not yet carried outbeen. By exploring prominent literature databases including PubMed and ScienceDirect, our aim is to write a narrative review to explore the individual ingredients of this blend and delve into their characteristics, as well as the most recent literature on their mechanism and efficacy in patients with osteoarthritis. Through this, we hope to inform clinicians and patients alike on relevant up-to-date research on the supplement and provide insight on the potential for this supplement for alleviating the disease course of patients with osteoarthritis.
Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;15():11795441211063365.
PMID: 35360183 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 14. |
Effect of Dietary Polyphenols on Osteoarthritis-Molecular Mechanisms.
Sirše M
Osteoarthritis is a common crippling and degenerative disease resulting in irreversible functional changes due to damage of the cartilage and other tissues of the joint. With limited safe and effective pharmaceutical treatments, the demand and use for alternative therapeutic approaches with symptomatic relief for OA patients have increased. Clinical, pre-clinical, and in vitro studies have demonstrated that polyphenols can exert pain-relieving symptoms coupled with increased functional capacity in OA models. This review will highlight studies carried out in the last five years to define the efficacies and underlying mechanisms in polyphenols such as quercetin, resveratrol, curcumin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate, rosmarinic acid, genistein, ginger, berries, silver fir, pine bark, and . Most of these studies indicate that polyphenols exhibit their beneficial roles through regulating changes at the biochemical and molecular levels, inducing or inhibiting various signaling pathways related to inflammation and oxidative stress. Polyphenols have also been implicated in modulating microRNA at the posttranscriptional level to counteract OA pathogenesis.
Life (Basel). 2022 Mar;12(3):.
PMID: 35330187 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 15. |
Efficacy of a dietary supplement in dogs with osteoarthritis: A randomized placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial.
Martello E, Bigliati M, Adami R, Biasibetti E, Bisanzio D, Meineri G, Bruni N
This study is a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded trial performed to investigate the effects of a dietary supplement containing a mixture of Boswellia serrata Roxb., chlorophyll, green tea extract, glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid, and further in the manuscript: non-hydrolised type II collagen in dogs with osteoarthritis (OA). A total of 40 dogs were enrolled in the study, they were randomly divided in control (CTR) and treatment (TRT) groups. The TRT group received the dietary supplement for 60 days. The CTR group received a placebo for the same number of days. All the subjects had veterinary evaluations during the trial and owners were requested to fill in questionnaires on chronic pain using the Helsinki Chronic Pain Index. The product was easy to administer and no side effects were reported. Combining results from veterinarian and owner evaluations, the tested product proved to be significantly beneficial in alleviating pain and in reducing the clinical signs in dogs with OA.
PLoS One. 2022;17(2):e0263971.
PMID: 35171954 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 16. |
Prospective, Multicenter Evaluation of a Polyherbal Supplement alongside Standard-of-Care Treatment for Mild Knee Osteoarthritis.
Żęgota Z, Goździk J, Głogowska-Szeląg J
BACKGROUND: This study aimed to provide clinical information on general and joint performance from individuals taking Tregocel® (containing curcuminoid and extracts of the herbs , , and ) alongside a standard therapy of symptomatic mild knee osteoarthritis (OA).
METHODS: This was a multicenter, open-label, prospective, single-arm study, in which Tregocel® was supplemented for 36 weeks. Participants with symptomatic mild knee OA requiring pharmacologic treatment for pain were enrolled. Physical performance (6-minute walk test, WOMAC-pain and functional domain, and heel-thigh distance flexion test), general performance (WOMAC questionnaire), and VAS (Visual Analogue Scale) assessment of knee pain, as well as anti-inflammatory and analgesic medication consumption, were assessed.
RESULTS: Between January and April 2019, 107 participants were enrolled and analysed in per protocol population. Mean age was 59.7 (SD 10.8) years, and there were 68.2% women. Mean observation time was 291.1 (SD 7.7) days. Mean increase in 6MWT result observed at the end of the study was 26.0 (SD 30.4) m ( < 0.001). Median VAS score decreased from 60.0 (IQR 50-72) mm at the beginning of the study to 21.0 (IQR 14-30) mm after 36 weeks of product administration ( < 0.001). Regular knee OA medications were taken in 99.1% of subjects at baseline decreasing to 55.1% at the end of the Tregocel® supplementation.
CONCLUSIONS: During Tregocel® supplementation, participants observed improved functional capacity confirmed in the distance in 6MWT and in the heel-thigh distance flexion test, decreased level of pain, and improved WOMAC scores for all domains.
Adv Orthop. 2021;2021():5589597.
PMID: 34035964 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 17. |
Efficacy and safety of a supplement combination on hand pain among people with symptomatic hand osteoarthritis an internet-based, randomised clinical trial the RADIANT study.
Liu X, Robbins S, Eyles J, Fedorova T, Virk S, Deveza LA, McLachlan AJ, Hunter DJ
OBJECTIVE: The RADIANT study aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of a complementary medicine supplement combination in people with hand osteoarthritis (HOA).
METHOD: This was an internet-based, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Participants aged over 40 years with symptomatic HOA with radiographic confirmation (Kellgren Lawrence grade ≥ 2) throughout Australia were recruited and randomly assigned (1:1) to receive either a supplement combination composed of Boswellia serrata extract 250 mg/day, pine bark extract 100 mg/day, methylsulfonylmethane 1,500 mg/day and curcumin 168 mg/day or placebo for 12 weeks. The primary outcome was change in hand pain assessed using a visual analogue scale (VAS 0-100) from baseline to week 12. A range of secondary outcomes and additional measures were recorded. Adverse events were monitored weekly.
RESULTS: One hundred and six participants were included with mean age 65.6 years and 81% were women. 45% of the participants were graded as KLG 4, 40% KLG three and 39 (37%) had erosive OA. There was no significant difference in pain VAS reduction between groups. The adjusted between group difference in means (95%CI) was 5.34 (-2.39 to 13.07). Five participants (10%) in the supplement combination group discontinued study treatment due to AE vs four participants (7%) in the placebo group.
CONCLUSION: There were no significant differences in symptomatic relief between the two groups over 12 weeks. These findings do not support the use of the supplement combination for treating hand pain in people with HOA.
REGISTRATION: Prospectively registered (Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry ACTRN12619000835145, 31/05/2019).
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021 May;29(5):667-677.
PMID: 33617972 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 18. |
Clusters of Responders and Predictive Factors for Response to Supplementation with Boswellia, Turmeric, and Red Algae Extracts in Painful Knee Osteoarthritis: A Prospective Observational Study Using an Arsenal of Patient-Centered Measures.
Ait Abdellah S, Gal C, Leblanc A, Trouvin AP, Perrot S
PURPOSE: This observational study evaluated a combination of boswellia, turmeric, and red algae extracts in patients with knee osteoarthritis (KOA). Given the growing interest in patient-centered care in osteoarthritis, effects were assessed by an arsenal of patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs): Patient Acceptable Symptom Scale (PASS), Minimal Clinically Important Improvement (MCII), Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC), and Lequesne algofunctional index (LAFI). Patients also completed a list of 17 items on pain quality.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Patients with painful unilateral or bilateral KOA had to take 1-4 capsules per day of a dietary supplement containing boswellia, turmeric, and red algae extracts for 90 days. Patients completed PROMs on Days 0 (baseline), 10, 20, 30, 60, and/or 90.
RESULTS: A total of 118 patients [female: 69.5%; age: 62.9 (9.5) years, mean (SD)] were included in the study and took at least one capsule. Mean (SD) follow-up duration was 100.7 (54.9) days. Pain relief was maximal on Day 90: 64.5% of patients were responders (positive PASS); 68.8% and 58.4% had MCII and PGIC scores indicating positive effect (score ≥3) or global improvement (score ≥5); 73.3% (versus 47.5% at baseline) were mildly/moderately disabled (LAFI score <8); 55.2% had meaningful decrease (-30%) in pain intensity (VAS), 35.1% (versus 59.2% at baseline) took analgesics as supplementary treatment. Median time to the first PASS change was 34 days. Pain intensity (VAS), as well as two pain characteristics (ie, "Stabbing pain" and "Widespread pain"), were independent factors associated with non-response on Day 30. Four clusters of responders were isolated according to pain characteristics, with one cluster exhibiting a higher responder rate.
CONCLUSION: The results of this preliminary study suggest that the combination of boswellia, turmeric, and red algae extracts tested could improve KOA patients. Beyond these results, this study showed the importance of PROMs and specific pain qualitative descriptors for the accurate evaluation of dietary supplement approaches in painful conditions.
Open Access Rheumatol. 2021;13():1-13.
PMID: 33447100 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 19. |
Curcuminoids and extracts combination decreases tendinopathy symptoms: findings from an open-label post-observational study.
Henrotin Y, Dierckxsens Y, Delisse G, Seidel L, Albert A
To investigate the effects of 1-month treatment in addition to standard care with a food supplement containing both and extracts on tendinopathy symptoms. This open-label, non-controlled, post-observational study included 670 patients suffering from tendinopathy recruited at different sites by Belgian general practitioners. Patients received a medical prescription for 1-month treatment with two tablets twice a day of a pharmaceutical grade food supplement containing both and extracts. Pain and functional limitation were evaluated using a visual analog scale at the inclusion and 1-month treatment later. Patient satisfaction, concomitant drugs intake and side effects were also recorded. After 1-month treatment, pain and functional limitation were significantly improved whatever the cause of tendinopathy, its localization, and the duration of symptoms. The pain score decreased from 6.16 ± 1.53 to 2.98 ± 1.64 ( < .0001), yielding a drop of 51.6% and the functional limitation score fell after 1-month treatment from 5.96 ± 1.73 to 2.88 ± 1.67 ( < .0001) corresponding to a drop of 51.6%. The percentage of patients taking at least one concomitant treatment at the end of the treatment period had decreased from 81.3% to 61.8% ( < .0001). Only 43 (6.5%) patients reported side effects. No severe adverse effects related to the product were reported. The combination of and extracts improves symptoms in patients suffering of tendinopathy and shows a good safety. Although its effect will have to be confirmed in randomized controlled trials, it can be considered as a helpful support of standard symptomatic treatments for tendinopathies. HighlightsTendinopathy is a common disease representing 30% of all consultations with a general practitioner for musculoskeletal disorders.The combination of Curcuminoids and extracts are efficient on tendinopathy symptoms in support of standard symptomatic treatments.The combination of Curcuminoids and extract is safe and can be administrated for at least 1 month in addition of analgesic and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Curr Med Res Opin. 2021 Mar;37(3):423-430.
PMID: 33287570 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 20. |
Supplementation with a new food grade delivery system of Boswellia and Centella in the intervertebral discs registry: the Sager study.
Morio H, Cesarone MR, Belcaro G, Feragalli B, Cotellese R, Hu S, Dugall M, Maione C, Scipione V, Scipione C, Riva A, Petrangolini G, Togni S
BACKGROUND: The aim of this registry study was to investigate the potential of a new food-grade formulation of the association of Boswellia serrata and Centella asiatica extracts (Boswellia/Centella Phytosome, [BCP]) in combination with standard management (SM) to produce a faster re-expansion of the intervertebral disks in symptomatic subjects with "flattened" disks in the lower spine, due to wrong posture and compression after repeated trauma.
METHODS: The study was designed as a 3-6 months pilot registry. Three groups of subjects were comparable for characteristics and symptoms at baseline: SM+BCP; SM; SM+glucosamine.
RESULTS: No side effects were observed. Regarding target measurements at 3 and 6 months, height increased in the BCP group vs. the other two groups. The total spine length improved in the BCP group (P<0.05); in particular at 6 months the increase was doubled with BCP. SM was effective in producing elongation but the association with BCP made spinal elongation faster, more effective, with a better expansion of the intervertebral disks. Regarding ultrasound measurements, BCP was able to significantly ameliorate the posterior disk space (P<0.05) and decreased disk density more than the other groups of the study. Signs/symptoms and mobility were improved with BCP (P<0.05), while rescue medications decreased. The loss of working days was reduced with all managements (significantly more in BCP group than in the other two).
CONCLUSIONS: The relative effects on spinal elongation, disk space, signs/symptoms of BCP appeared to double the efficacy of SM, improving symptoms associated to a very good tolerability of BCP.
Panminerva Med. 2022 Mar;64(1):48-55.
PMID: 32894920 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 21. |
A sport cream (Harpago-Boswellia-ginger-escin) for localized neck/shoulder pain.
Hu S, Belcaro G, Cesarone MR, Feragalli B, Cotellese R, Dugall M, Scipione C, Scipione V, Maione C, Maramaldi G, Togni S, Riva A
BACKGROUND: Neck/shoulder, sudden pain, or muscular pain (not associated to structural or bone/joints components), due to fascial or muscular strain is common in active subjects, in non-professional athletes and sports performers. The aim of this supplement registry was the evaluation of a cream based on natural, active ingredients for topical application in supporting the improvement of pain and improving head/neck mobility, possibly minimizing the use of systemic drugs.
METHODS: The cream includes standardized active ingredients of natural origin as an extract of Harpagophytum procumbes, an extract from Boswellia serrata, a CO2 extract of ginger and escin. Subjects were divided into three groups, all using the standard management (SM) in combination with the Sport Cream or in addition to Flector (diclofenac) patch.
RESULTS: The groups were comparable and homogeneous at the baseline. No side effects or skin tolerability issues were observed with the Sport Cream nor with the SM or diclofenac patches. Subjects receiving sport cream + SM reported a significant improvement in pain, stiffness, altered mobility and altered working capacity, with a reduced need for rescue medication (diclofenac) compared to subjects in the other two groups.
CONCLUSIONS: Finally, subjects receiving sport cream + SM reported a more remarkable decrease in skin temperature in the affected area associated to an improvement in clinical symptoms.
Minerva Med. 2021 Apr;112(2):255-260.
PMID: 32880419 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 22. |
Effectiveness of Boswellia and Boswellia extract for osteoarthritis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Yu G, Xiang W, Zhang T, Zeng L, Yang K, Li J
BACKGROUND: Osteoarthritis (OA) is the commonest form of inflammatory joint disease. Unfortunately, to date, there is no appropriate treatment for OA. Boswellia serrata was considered as a potent anti-inflammatory, anti-arthritic and analgesic agent that may be a drug for OA.
METHODS: In this meta-analysis, data from randomized controlled trials were obtained to assess the effects of Boswellia or its extract versus placebo or western medicine in patients with OA. The primary outcomes included visual analogue score (VAS), WOMAC pain, WOMAC stiffness, WOMAC function and lequesne index.
RESULT: Seven trials involving 545 patients were included. Compared with the control group, Boswellia and its extract may relieve the pain [VAS: (WMD -8.33; 95% CI -11.19, - 5.46; P<0.00001); WOMAC pain: (WMD -14.22; 95% CI -22.34, - 6.09; P = 0. 0006)] and stiffness [WOMAC stiffness: (WMD -10.04; 95% CI -15.86, - 4.22; P = 0. 0007)], and improve the joint's function [WOMAC function: (WMD -10.75; 95% CI -15.06, - 6.43; P<0. 00001); lequesne index: (WMD -2.27; 95% CI -3.08, - 1.45; P<0. 00001)].
CONCLUSION: Based on current evidence, Boswellia and its extract may be an effective and safe treatment option for patient with OA, and the recommended duration of treatment with Boswellia and its extract is at least 4 weeks.
BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Jul;20(1):225.
PMID: 32680575 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 23. |
Efficacy of high-dissolution turmeric-sesame formulation for pain relief in adult subjects with acute musculoskeletal pain compared to acetaminophen: A randomized controlled study.
Rudrappa GH, Chakravarthi PT, Benny IR
BACKGROUND: Acetaminophen (paracetamol) is one of the most commonly used over-the-counter for pain relief. Management of acute pain with plant-based nutrients has remained suboptimal due to an absence of data supporting acute relief of pain. In the present study, it was hypothesized that high-dissolution liquid treatment of black sesame extract oil, Curcuma longa and Boswellia serrata may provide pain relief in people with acute musculoskeletal pain as quickly as acetaminophen.
METHODS: In this randomized active controlled open label study, 88 healthy subjects with acute musculoskeletal pain were randomized to receive treatment capsule (Rhuleave-K; 1,000 mg/d) or 1,000 mg/d acetaminophen for 7 days. Change in pain intensity and pain relief at first 6 hours, 3 days, and 7 days were measured. The onset of analgesia was measured by perceptible pain relief and meaningful pain relief. Other measures were McGill Pain Questionnaire and Patient Global Impression Change.
RESULTS: The treatment formulation resulted in average magnitude of pain relief comparable to the acetaminophen. Sixty-six percent of subjects in the treatment group reported positive response in pain relief (≥50% max TOTPAR; total pain relief) after 6 hours, compared to 73% of control. Seventy-three percent of subjects on treatment were considered positive responders, compared to 80% in the control group. The average time of onset of analgesia was 1 hour for the treatment group, versus 0.83 hour for control. At the end of day 3 and 7, there was significant improvement (P < .001 for day 3 and day 7) in the pain condition of treatment group and was comparable to control (P = .436 for day 3 and P = .529 for day 7). The total McGill Pain score showed significant reduction in pain with the treatment irrespective of the pain intensity statistically equal (P = .468) to control. Both the groups were equal in providing sensory pain relief (P = .942), but the treatment was 8.57 times significantly better (P = .027) than acetaminophen in reducing the unpleasantness and emotional aspects (affective domain) involved with acute pain.
CONCLUSION: The results showed that the treatment used in the study may act as a natural, fast acting, and safe alternative for acute pain relief comparable to acetaminophen.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jul;99(28):e20373.
PMID: 32664057 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 24. |
Double-blind trial of solid lipid Boswellia serrata particles (SLBSP) vs. standardized Boswellia serrata gum extract (BSE) for osteoarthritis of knee.
Kulkarni PD, Damle ND, Singh S, Yadav KS, Ghante MR, Bhaskar VH, Hingorani L, Gota VS
Objectives The present study was planned to investigate the efficacy of SLBSP vs. standardized BSE for symptomatic knee osteoarthritis (OA) treatment. Methods It was a prospective, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, and single-centre clinical trial for symptomatic osteoarthritis of knee. Subjects were randomized to receive SLBSP capsule+BSE Placebo or BSE tablet+SLBSP placebo for two months. Patients were allowed to take rescue analgesics (Acelofenac 100 mg). Improvement in pain and function was assessed utilizing WOMAC, VAS. Level of CTX-II in urine and serum levels of inflammatory cytokines including IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ was measured initially and at end of treatment. Results and conclusions Western Ontario and McMaster Universities osteoarthritis index (WOMAC) and Visual Analog Scale score improved markedly in SLBSP as well as in BSE arm (p < 0.05). Difference in VAS and WOMAC scores between the two arms was not statistically significant. Most significant effect was observed in the need for rescue analgesics. SLBSP caused marked lowering of pro-inflammatory cytokines levels whereas a several fold increase was noted in the BSE arm (p < 0.05). Both groups showed marked improvement in pain, SLBSP being superior to BSE with respect to reducing the need for rescue analgesics in addition to modulating inflammatory cytokines.
Drug Metab Pers Ther. 2020 Jun;35(2):.
PMID: 32549135 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 25. |
Efficacy and safety of a supplement combination for hand osteoarthritis pain: protocol for an internet-based randomised placebo-controlled trial (The RADIANT study).
Liu X, Robbins S, Eyles J, Fedorova T, Virk S, Deveza LA, McLachlan A, Hunter D
INTRODUCTION: Hand osteoarthritis (HOA) is a highly prevalent disabling joint disease. The current management regimens are limited. Potentially as a consequence, many people turn to complementary and alternative medicines for symptomatic relief. A combination of two or more supplements is common in clinical practice; however, evidence for the efficacy of this approach is lacking. The aim of this study is to investigate the efficacy of a supplement combination for treating symptomatic HOA in comparison to placebo.
METHODS AND ANALYSIS: The RADIANT study is an internet-based, parallel, superiority, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, two-arm clinical trial. A participatory design is used to facilitate the study procedures. One hundred and six participants aged over 40 years with painful HOA and structural change on X-ray (Kellgren and Lawrence grade (KLG) ≥2) will be recruited from the community and randomly allocated to receive either a supplement combination composed of: (1) combined supplement containing extract, pine bark extract and methylsulfonylmethane and (2) curcumin or placebo for 12 weeks. The primary outcome will be 12-week change in hand pain on a visual analogue scale (VAS). Main secondary outcomes include adverse events, change in hand function, patient global assessment of disease activity and quality of life. A range of additional measures will be recorded, and an individual patient placebo response will be performed. The primary analysis will be conducted using an intention-to-treat approach. Adverse events will be monitored weekly throughout the study.
ETHICS AND DISSEMINATION: This protocol has been approved by the University of Sydney Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC No. 2018/766). Dissemination will occur through conferences, social media, scientific publications and PhD thesis.
TRIAL REGISTRATION NUMBER: Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (ACTRN12619000835145); Pre-results.
BMJ Open. 2020 Feb;10(2):e035672.
PMID: 32075845 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 26. |
Effect Of E-OA-07 On Improving Joint Health And Mobility In Individuals With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel Group Study.
Srivastava S, Chaudhary JA, Girandola RN
AIM: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of E-OA-07 on individuals having osteoarthritis of the knee.
BACKGROUND: Lanconone (E-OA-07) is a widely marketed dietary supplement which has been previously studied in different clinical settings for managing chronic joint pain. This was a confirmatory study planned at a lowered dose regimen with the purpose of improving compliance and reducing consumer cost.
METHODS: Male and female participants aged between 40 and 65 years, with history of joint pain for at least 3 years, were recruited. Knee joint dysfunction of grade II/III was radiographically characterized as per Kellgren-Lawrence system of classification. Enrolled participants were randomized to receive E-OA-07 at a dose of 1000 mg/day or placebo over a period of 8 weeks. The primary efficacy parameter was assessment of change in Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain score. Whereas, the secondary parameters explored in the study included WOMAC subscales of stiffness and physical function, EQ-5D-5L questionnaire, systemic inflammatory marker (hs-CRP) and self-assessment of treatment satisfaction.
RESULTS: At the end of 8 weeks, joint pain severity as per WOMAC was found to be significantly reduced in the E-OA-07 group as compared to placebo (p<0.001). Similar improvement was observed in the subscales of stiffness and physical function which corresponds to significant improvement in the quality-of-life standards of E-OA-07 participants (p<0.001), reporting higher treatment satisfaction (p<0.001).
CONCLUSION: E-OA-07 at a dose of 1000 mg/day was able to significantly reduce joint pain and thereby improve joint mobility in study participants. At the end of the study period, there was a clinically relevant change of 45.55%, 45.91% and 38.19% for pain, stiffness and physical function, respectively. Moving forward, studies could be planned for understanding the cartilage regenerative properties of E-OA-07.
J Pain Res. 2019;12():3365-3379.
PMID: 31908521 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 27. |
Benefits of a Food Supplement Containing and Bromelain for Improving the Quality of Life in Patients with Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Study.
Italiano G, Raimondo M, Giannetti G, Gargiulo A
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a joint disease involving articular cartilage degeneration causing patients pain, joint stiffness, physical disability, and significantly reducing their quality of life (QoL). The aim of this study was to assess whether the daily consumption of a gastroresistant food supplement formulation containing a combination of B and bromelain could improve the QoL of patients suffering from various forms of OA. Forty-nine patients were enrolled in this pilot study conducted from June 2015 to October 2016. Patients took a Boswellia- and bromelain-based supplement for a period between 1 and 6 months. At baseline and at the end of the study, patients completed a self-assessment QoL questionnaire regarding their independence in performing daily activities. QoL scores were compared between baseline and follow-up by means of the Wilcoxon signed-rank test in all patients and in the subgroups of patients with knee, hip, or generalized OA. Forty-nine patients, 6 men and 43 women, aged between 23 and 92 years, (mean age 63.24) participated in the study. At follow-up (3.0 ± 0.7 months), a significant improvement was observed for 7 of 10 QoL questions and, overall, for the total QoL score. The most significant improvements were observed in the joints that were more strongly affected at baseline. A similar trend was observed when separately considering patients with knee, hip, or generalized OA. No patients experienced adverse events and no drug interactions were reported. From this pilot study, it emerges that the use of the gastroresistant formulation containing the combination of Boswellia and bromelain supplements can represent a valuable nonpharmacological tool for improving the QoL of patients suffering from different forms of OA. Further studies should be conducted to confirm this first evidence.
J Altern Complement Med. 2020 Feb;26(2):123-129.
PMID: 31674795 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 28. |
Pumpkin seeds, Centella asiatica, Boswellia, Helichrysum, acetate vitamin E, Melaleuca alternifolia and hyaluronic acid phytocomplex monotherapy effects in patients with chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
Di Vico T, Durante J, Polito C, Tognarelli A, Canale D, Caglieresi C, Morelli G, Bartoletti R
BACKGROUND: Proxelan® and antibiotics combined therapy was successfully previously used in the treatment of symptoms of patients with chronic prostatitis. Aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of Proxelan® monotherapy on pain symptoms of patients with chronic prostatitis (CP) or chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) in a prospective pilot study.
METHODS: Thirty consecutive patients with CP/CPPS symptoms younger than 50, without urinary obstruction, total prostate-specific antigen (PSA) <4 ng/mL, negative microbiology testing on prostate fluid and urethral swab, naïve from other treatments during the previous three months were enrolled in a pilot study. IPSS and NIH-CPSI questionnaires were administered to all the patients. Patients could choose to be investigated regarding semen quality and IL6/IL8 seminal markers for inflammatory disease prior and after the therapy course. Proxelan® suppositories were prescribed for each patient for a month with a daily dosage of 1 suppository at bed-time. The primary endpoint of the study included at least a 30% reduction of pain symptoms because similar results can be obtained in each previously investigated placebo group. Effects on semen parameters such as leukocytospermia, spermatozoa concentration and motility, cytokine levels were considered as secondary endpoints.
RESULTS: Subjective pain relief was obtained in all the patients with significant decrease of NIH-CPSI pain items (P=0.04). Urinary symptoms, investigated by IPSS questionnaire, decreased significantly (P=0.04) as well as quality of life items (P=0.04). Leukocytospermia was found in 5/15 patients available for further investigations. IL6 decreased by 11.55% one month after the treatment while sperm motility resulted increased by 17.3%.
CONCLUSIONS: Proxelan® monotherapy may represents a promising valid alternative to combined treatment with antibiotics in patients with CP/CPPS symptoms although the results obtained should be investigated in randomized controlled trials.
Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2020 Apr;72(2):236-242.
PMID: 31558010 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 29. |
A pilot, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to assess the safety and efficacy of a novel Boswellia serrata extract in the management of osteoarthritis of the knee.
Majeed M, Majeed S, Narayanan NK, Nagabhushanam K
A double-blind, placebo-controlled human trial was conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a standardized oral supplementation of Boswellin®, a novel extract of Boswellia serrata extract (BSE) containing 3-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBBA) with β-boswellic acid (BBA). A total of 48 patients with osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee were randomized and allocated to the BSE and placebo groups for intervention. Patients were administered BSE or placebo for a period of 120 days. The trial results revealed that BSE treatment significantly improved the physical function of the patients by reducing pain and stiffness compared with placebo. Radiographic assessments showed improved knee joint gap and reduced osteophytes (spur) confirming the efficacy of BSE treatment. BSE also significantly reduced the serum levels of high-sensitive C-reactive protein, a potential inflammatory marker associated with OA of the knee. No serious adverse events were reported. This is the first study with BSE conducted for a period of 120 days, longer than any other previous clinical trial on patients with OA of the knee. The findings provide evidence that biologically active constituents of BSE, namely, AKBBA and BBA, act synergistically to exert anti-inflammatory/anti-arthritic activity showing improvement in physical and functional ability and reducing the pain and stiffness.
Phytother Res. 2019 May;33(5):1457-1468.
PMID: 30838706 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 30. |
An Anecdote About Arthritis and Boswellia serrata.
Shader RI
Clin Ther. 2018 May;40(5):669-671.
PMID: 29735296 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 31. |
A Placebo-Controlled Double-Blind Study Demonstrates the Clinical Efficacy of a Novel Herbal Formulation for Relieving Joint Discomfort in Human Subjects with Osteoarthritis of Knee.
Karlapudi V, Prasad Mungara AVV, Sengupta K, Davis BA, Raychaudhuri SP
LI73014F2 is a novel composition prepared from extracts of Terminalia chebula fruit, Curcuma longa rhizome, and Boswellia serrata gum resin with synergistic benefit in 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LOX) inhibition. This herbal composition with strong anti-5-LOX activity exhibited significant pain relief as indicated through improvements in weight-bearing capacity in a monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis (OA) model of Sprague-Dawley rats. A 90-day randomized, placebo-controlled double-blind study evaluates the clinical efficacy and tolerability of LI73014F2 in the management of symptoms of OA of the knee (Clinical Trial Registration No. CTRI/2014/01/004338). Subjects, (n = 105), were randomized into three groups: placebo (n = 35), 200 mg/day of LI73014F2 (n = 35), and 400 mg/day of LI73014F2 (n = 35). All study participants were evaluated for pain and physical function by using standard tools, that is, Visual Analog Scale, Lequesne's Functional Index, and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) at the baseline (day 0) and on day 14 ± 3, 30 ± 3, 60 ± 3, and at the end of the study (day 90 ± 3). In addition, routine examinations on biochemical parameters in serum, urine, and hematological parameters were conducted on each visit to assess the safety of the study material. At the end of the trial period, LI73014F2 conferred significant pain relief, improved physical function, and quality of life in OA patients. In conclusion, preclinical and clinical data together strongly suggest that the herbal formulation LI73014F2 is a safe and effective intervention for management of joint discomfort, demonstrating efficacy as early as 14 days.
J Med Food. 2018 May;21(5):511-520.
PMID: 29708818 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 32. |
Efficacy of curcumin and Boswellia for knee osteoarthritis: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Bannuru RR, Osani MC, Al-Eid F, Wang C
PURPOSE: The unfavorable safety profiles of commonly prescribed knee osteoarthritis (OA) treatments have led clinicians and patients to seek safer alternatives. Research has suggested that curcuminoid and boswellia formulations could moderate key inflammatory pathways that are associated with worsening symptoms and disease progression. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the efficacy and safety of these treatments vs. placebo or NSAIDs for knee OA.
METHODS: We searched Medline, EMBASE, Google Scholar, Web of Science and the Cochrane database from inception to February 21, 2018. We also hand searched reference lists and reviewed conference proceedings. We included randomized clinical trials (RCTs) comparing curcuminoid or boswellia formulations with placebo or NSAIDs for knee OA. We calculated standardized mean differences (SMD) or risk ratios (RR) for all relevant outcomes. Meta-analyses were conducted using random effects models. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I statistic.
RESULTS: Eleven RCTs (N = 1009) were eligible for analysis. Study quality was low overall, and most included RCTs were conducted on fewer than 100 participants. Both curcuminoid and boswellia formulations were statistically significantly more effective than placebo for pain relief and functional improvement. There were no significant differences between curcuminoids or boswellia and placebo in safety outcomes. Curcuminoids showed no statistically significant differences in efficacy outcomes compared to NSAIDs; patients receiving curcuminoids were significantly less likely to experience gastrointestinal adverse events. No RCTs compared boswellia against approved NSAIDs.
CONCLUSIONS: The results of our study suggest that curcuminoid and boswellia formulations could be a valuable addition to the knee OA treatment regimens by relieving symptoms while reducing safety risks. The current body of evidence is not adequate in size or quality to make any meaningful clinical practice recommendations. Further research through large, high quality RCTs probably investigating the synergistic effect of these products with other OA treatments is warranted.
Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2018 Dec;48(3):416-429.
PMID: 29622343 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 33. |
Phytoproflex®: supplementary management of osteoarthrosis: a supplement registry.
Belcaro G, Dugall M, Luzzi R, Hosoi M, Ledda A, Feragalli B, Hu S, Ganguly A, Eggenhoffner R, Corti A, Giacomelli L
BACKGROUND: Curcumin is a powerful anti-oxidant that can be used to treat inflammation and pain in chronic conditions such as osteoarthrosis (OA). Phytoproflex® is characterized by an innovative delivery system that improves bioavailability of curcuminoids and could be useful in the management of OA.
METHODS: This 4-week registry included 56 patients with knee OA treated according to the best standard management for symptomatic OA. On top of that, 24 patients used Phytoproflex® supplement preparation (an extract containing boswellic acid 90%, curcumin 20% and valeric acid 0.8%). Patients' control of symptoms and functional capacity were evaluated through the Karnofsky Scale and standardized treadmill test, together with measurement of oxidative stress levels and use of rescue medication.
RESULTS: No problems of tolerability or safety were reported among subjects using the supplement. After 4 weeks, patients treated with the supplement reported a significant decrease in pain (P<0.05), and a significant improvement in the fitness scale (P<0.05), indicating that subjects were able to perform normal daily tasks. Less subjects in the supplement group had to use rescue medication (P<0.05), while oxidative stress levels, which were high at inclusion, significantly decreased in both groups (P<0.05). Moreover, the variation in pain-free walking distance and the Karnofsky Scale were significantly more improved (P<0.05) in patients taking the supplement compared to controls.
CONCLUSIONS: This preliminary registry study indicates that Phytoproflex® can be safely used as an effective, supplementary management in most OA patients.
Minerva Med. 2018 Apr;109(2):88-94.
PMID: 29534559 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 34. |
Efficacy and safety of curcumin and its combination with boswellic acid in osteoarthritis: a comparative, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Haroyan A, Mukuchyan V, Mkrtchyan N, Minasyan N, Gasparyan S, Sargsyan A, Narimanyan M, Hovhannisyan A
BACKGROUND: The aim of this clinical trial was to assess the efficacy and safety of curcuminoid complex extract from turmeric rhizome with turmeric volatile oil (CuraMed®) and its combination with boswellic acid extract from Indian frankincense root (Curamin®) vs placebo for the treatment of 40- to 70-year-old patients with osteoarthritis (OA).
METHODS: The effects of CuraMed® 500-mg capsules (333 mg curcuminoids) and Curamin® 500-mg capsules (350 mg curcuminoids and 150 mg boswellic acid) taken orally three times a day for 12 weeks in 201 patients was investigated in a three-arm, parallel-group, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Primary outcome efficacy measures included OA physical function performance-based tests, the WOMAC recommended index of joint pain, morning stiffness, limitations of physical function, and the patients' global assessment of disease severity.
RESULTS: Favorable effects of both preparations compared to placebo were observed after only 3 months of continuous treatment. A significant effect of Curamin® compared to placebo was observed both in physical performance tests and the WOMAC joint pain index, while superior efficacy of CuraMed vs placebo was observed only in physical performance tests. The effect size compared to placebo was comparable for both treatment groups but was superior in the Curamin® group. The treatments were well tolerated.
CONCLUSIONS: Twelve-week use of curcumin complex or its combination with boswellic acid reduces pain-related symptoms in patients with OA. Curcumin in combination with boswellic acid is more effective. Combining Curcuma longa and Boswellia serrata extracts in Curamin® increases the efficacy of OA treatment presumably due to synergistic effects of curcumin and boswellic acid.
TRIAL REGISTRATION: This trial is registered at the database www.clinicaltrials.gov . https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02390349?term=EuroPharma&rank=1 . Study registration number: NCT02390349 .
BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Jan;18(1):7.
PMID: 29316908 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 35. |
Dietary supplements for treating osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Liu X, Machado GC, Eyles JP, Ravi V, Hunter DJ
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the efficacy and safety of dietary supplements for patients with osteoarthritis.
DESIGN: An intervention systematic review with random effects meta-analysis and meta-regression.
DATA SOURCES: MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Register of Controlled Trials, Allied and Complementary Medicine and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature were searched from inception to April 2017.
STUDY ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA: Randomised controlled trials comparing oral supplements with placebo for hand, hip or knee osteoarthritis.
RESULTS: Of 20 supplements investigated in 69 eligible studies, 7 (collagen hydrolysate, passion fruit peel extract, extract, extract, curcumin, pycnogenol and L-carnitine) demonstrated large (effect size >0.80) and clinically important effects for pain reduction at short term. Another six (undenatured type II collagen, avocado soybean unsaponifiables, methylsulfonylmethane, diacerein, glucosamine and chondroitin) revealed statistically significant improvements on pain, but were of unclear clinical importance. Only green-lipped mussel extract and undenatured type II collagen had clinically important effects on pain at medium term. No supplements were identified with clinically important effects on pain reduction at long term. Similar results were found for physical function. Chondroitin demonstrated statistically significant, but not clinically important structural improvement (effect size -0.30, -0.42 to -0.17). There were no differences between supplements and placebo for safety outcomes, except for diacerein. The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation suggested a wide range of quality evidence from very low to high.
CONCLUSIONS: The overall analysis including all trials showed that supplements provided moderate and clinically meaningful treatment effects on pain and function in patients with hand, hip or knee osteoarthritis at short term, although the quality of evidence was very low. Some supplements with a limited number of studies and participants suggested large treatment effects, while widely used supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin were either ineffective or showed small and arguably clinically unimportant treatment effects. Supplements had no clinically important effects on pain and function at medium-term and long-term follow-ups.
Br J Sports Med. 2018 Feb;52(3):167-175.
PMID: 29018060 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 36. |
Oral herbal medicines marketed in Brazil for the treatment of osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Del Grossi Moura M, Lopes LC, Biavatti MW, Kennedy SA, de Oliveira E Silva MC, Silva MT, de Cássia Bergamaschi C
Herbal medications are commonly used to manage symptoms associated with osteoarthritis (OA). This systematic review evaluated the effectiveness and safety of oral medications used in Brazil for the treatment of OA. Randomized clinical trials involving adults with OA treated by a herbal medicine or a control group were eligible. The primary outcomes measured were pain, physical function, swelling, stiffness and quality of life; and the secondary outcomes were adverse events, activity limitations and treatment satisfaction. Sixteen studies were included (n = 1,741 patients) in the systematic review and nine studies in the meta-analysis, representing 6 of the 13 herbal medicines studied: Boswellia serrata (n = 2), Curcuma longa (n = 3), Harpagophytum procumbens (n = 1), Salix daphnoides (n = 3), Uncaria guianensis (n = 2) and Zingiber officinale (n = 5). B. serrata was more effective than both placebo and valdecoxib for improvement of pain and physical function. No difference was observed for H. procumbens, C. longa and U. guianensis compared with control. Z. officinale showed improvement of pain over placebo. The evidence was insufficient to support the effective and safe use of these herbal medicines, because the quality of evidence of studies was low. This study guides managers of the Brazilian public health system and prescribers in decision-making regarding the use of these herbal medicines for OA. Copyright © 2017 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Phytother Res. 2017 Nov;31(11):1676-1685.
PMID: 28872719 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 37. |
Evaluation of the effect of Elaeagnus angustifolia alone and combined with Boswellia thurifera compared with ibuprofen in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized double-blind controlled clinical trial.
Karimifar M, Soltani R, Hajhashemi V, Sarrafchi S
Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the most common articular disorders. Many patients do not respond to acetaminophen and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the mainstay of pharmacotherapy for knee OA. The plants Elaeagnus angustifolia and Boswellia thurifera have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of E. angustifolia alone and in combination with B. thurifera compared with ibuprofen in patients with knee osteoarthritis. In a randomized double-blind controlled clinical trial, 75 patients with knee OA were randomly and equally assigned to one of three groups Elaeagnus (n = 23), Elaeagnus/Boswellia (n = 26), and ibuprofen (n = 26) to receive the capsules of Elaeagnus, Elaeagnus/Boswellia, and ibuprofen, respectively, three times daily with meals for 4 weeks. Pain severity based on VAS (visual analog scale, 0 to 10 scale) and the scores of LPFI (Lequesne Pain and Function Index) and PGA (patient global assessment) were determined pre- and post-intervention for all patients. All interventions had significant lowering effects on VAS, LPFI, and PGA scores (P < 0.001 for all parameters) with no significant difference between groups in terms of effects on all evaluated parameters. Consumption of E. angustifolia fruit extract either alone or in combination with Boswellia oleo-gum resin extract could decrease pain and improve function in patients with knee osteoarthritis comparable to ibuprofen.
Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Aug;36(8):1849-1853.
PMID: 28349271 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 38. |
Phytomedicine in Joint Disorders.
Dragos D, Gilca M, Gaman L, Vlad A, Iosif L, Stoian I, Lupescu O
Chronic joint inflammatory disorders such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis have in common an upsurge of inflammation, and oxidative stress, resulting in progressive histological alterations and disabling symptoms. Currently used conventional medication (ranging from pain-killers to biological agents) is potent, but frequently associated with serious, even life-threatening side effects. Used for millennia in traditional herbalism, medicinal plants are a promising alternative, with lower rate of adverse events and efficiency frequently comparable with that of conventional drugs. Nevertheless, their mechanism of action is in many cases elusive and/or uncertain. Even though many of them have been proven effective in studies done in vitro or on animal models, there is a scarcity of human clinical evidence. The purpose of this review is to summarize the available scientific information on the following joint-friendly medicinal plants, which have been tested in human studies: spp., spp., , spp., , , , , and .
Nutrients. 2017 Jan;9(1):.
PMID: 28275210 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 39. |
Five Herbs Plus Thiamine Reduce Pain and Improve Functional Mobility in Patients With Pain: A Pilot Study.
Hedaya R
UNLABELLED: Context • Five herbs-Urtica dioica (stinging nettle), Boswellia serrata, Equisetum arvense, Allium sativum, and Apium graveolens-have been demonstrated to have activity at several anti-inflammatory pathways and have analgesic properties that are effective in treating chronic musculoskeletal pain. Objectives • The study intended to evaluate the clinical efficacy of a proprietary blend of U dioica, B serrata, E arvense, A sativum, A graveolens, and thiamine (vitamin B1), or "the blend," in the treatment of chronic musculoskeletal pain. Methods • The research team performed a prospective case study. Setting • The study took place at the National Center for Whole Psychiatry in Chevy Chase, MD, USA.
PARTICIPANTS: Participants were patients who had experienced baseline persistent musculoskeletal pain for at least 4 mo in ≥1 body parts without relief from traditional treatments. Intervention • Participants were provided with a 14-d supply of the study's medication. Two 350-mg capsules were administered 2 ×/d with food. The participants were instructed not to alter or add any therapies for their pain-associated condition for the 14 d of the study. Outcome Measures • The primary outcome measure was the change on a subjectively scored visual analogue scale (VAS), similar to the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index. The VAS was used to assess pain and the impact of motion and mobility at each location with pain. Each patient was administered the VAS rating scale to assess physical function and pain status at baseline and at the end of 14 d or postintervention. Patients were seen for follow-up at a minimum of 2 wk and underwent an interview, with the VAS rating scale being readministered. Results • A total of 13 patients, involving 27 pain sites, qualified for the study, 5 males and 8 females with a median age of 58 y. The primary sites of pain were (1) the knees-5 sites (18.5%), (2) the shoulders-6 sites (16.6%), and (3) the back (sciatica)-5 sites (18.5%), with 11 miscellaneous locations (40.7%) making up the rest of the sites, including the neck, jaw, foot, heel, and coccyx. The mean disease duration was 5.61 y, with a range of 4 mo to 20 y. The average VAS pain subscale score was 58.04 at baseline and 23.33 at follow-up. The mean difference between the 2 scores was 34.71 (confidence interval [CI], 26.16-47.01). A significant reduction in the pain scores had occurred by the follow-up assessment (t = 7.23, P < .05). The average VAS subscale score for functional mobility was 56.67 at baseline and 28.70 at follow-up. The mean difference between the 2 mobility scores was 27.97 (CI, 17.86-38.88). A significant improvement in the ability to move had occurred in the affected areas by the follow-up assessment (t = 5.97, P < .05). No adverse effects were reported. Conclusions • A clinically significant reduction in perceived pain and improvement in functional mobility had occurred for the intervention group as related to their chronic joint, back, and muscle pain. The complex of 5 herbs, plus vitamin B1, was well tolerated, and the results suggest that the blend should be considered to be a valuable alternative treatment in the management of chronic musculoskeletal pain.
Altern Ther Health Med. 2017 Jan;23(1):14-19.
PMID: 28160759 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 40. |
Movardol® (N-acetylglucosamine, Boswellia serrata, ginger) supplementation in the management of knee osteoarthritis: preliminary results from a 6-month registry study.
Bolognesi G, Belcaro G, Feragalli B, Cornelli U, Cotellese R, Hu S, Dugall M
OBJECTIVE: Knee Osteoarthritis (OA) is a chronic disease caused by the deterioration of cartilage in joints, which results in activation of the inflammatory response, pain, and impaired movement. Complementary therapies, particularly supplementation, in the management of moderate/severe knee OA have been gaining attention. This registry study aimed at evaluating the synergistic effect of Movardol®, a supplementation containing active ingredients with recognized anti-inflammatory activities on symptoms and levels of circulating biomarkers of knee OA.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: 54 subjects with symptomatic, moderate knee OA freely decided to follow either a standard management (SM) (n = 26) or SM plus oral supplementation with Movardol® (n = 28). Movardol® supplementation containing N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, ginger, and Boswellia Serrata extract was taken at the following dosage: 3 tablets/day for one week and then 2 tablets/day. Several parameters were assessed at inclusion and after 1, 3 and 6 months: functional impairment by the Karnofsky Performance Scale Index; pain, stiffness, physical, social and emotional functions by the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC); total and pain-free walking distance; circulating biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress.
RESULTS: Significant improvements in the functional outcomes and pain-free walking distance were observed after 1, 3 and 6 months in OA patients supplemented with Movardol®. Moreover, all the signs/symptoms of disease assessed by the WOMAC tended to regress over a 6-month period in patients following SM+supplementation. Inflammatory markers and plasmatic content of reactive oxygen species decreased over 6 months, in supplemented patients. Movardol® supplementation resulted to be safe and well tolerated, also showing the beneficial effect in term of a decrease in pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments and, consequently, reduction in management costs.
CONCLUSIONS: These preliminary results indicate the efficacy and safety of Movardol® supplementation in the management of moderate knee OA.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Dec;20(24):5198-5204.
PMID: 28051248 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 41. |
Management strategies for knee osteoarthritis: Aflapin ().
Suva MA, Kheni DB, Sureja VP
Ayu. 2017;38(1-2):94.
PMID: 29861602 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 42. |
In Vivo Osteoinduction: Evaluating 2-Beta Coxatene as an Immunoinductive Compound and Novel Ingredient for Joint Support.
Spinks K, Scaffidi JJ
CONTEXT: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease characterized by progressive loss of articular cartilage. Many treatments lack the ability to stimulate the growth of native cartilage tissue while they simultaneously increase joint comfort. For the past few decades, dietary supplements have been investigated for the ability to both address joint inflammation and stimulate cartilage tissue.
OBJECTIVES: The present study intended to examine the supplement's in vivo osteoinductive capabilities and clinical efficacy for overall joint health.
DESIGN: The research team designed a randomized, double-blind, comparative clinical trial.
SETTING: The study took place via telephone interviews.
PARTICIPANTS: Participants had self-reported OA of a weight-bearing joint (ie, of the knee, hip, spine, or ankle). Patients were recruited using the Health Science Institute, a consumer supplement newsletter.
INTERVENTION: Participants in the intervention group were blindly given 135 mg of 2-Beta Coxatene (2BCT) orally, which contained (1) a custom blend of low-dose Cyplexinol, an osteoinductive protein complex derived from bovine bone tissue, and (2) resin enriched to 65% 3--Acetyl-11-keto-β-Boswellic acid. A positive control group was blindly given 1500 mg of glucosamine hydrogen chloride and 1200 mg of chondroitin sulfate. Participants took the supplements for 3 mo.
OUTCOME MEASURES: A histological evaluation was performed on an athymic rat to test the supplement's in vivo osteoinductive capabilities. A negative control, commercially purchased, unhydrolyzed type 2 collagen was used for that test. Participants were evaluated for parameters of pain and joint function at baseline (day 0) and at days 7, 30, and 90 using the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities (WOMAC) OA index and a visual analogue scale (VAS).
RESULTS: The histological evaluation of the athymic rat confirmed that the Cyplexinol component of the 2BCT was positive for de novo bone tissue and collagen synthesis, corroborating osteoinduction. In the clinical trial, the intervention group reported significant decreases of 57.4%, 52.5%, and 58% in normalized WOMAC scores for pain, stiffness, and joint functionality, respectively, from baseline to postintervention. The control group reported a decrease of 17.5%, 18.1%, and 23.9% for pain, stiffness, and joint functionality, respectively. For the intervention group, pain intensity and frequency, as measured by the VAS, also decreased 57.1% and 56.3%, respectively, from baseline to postintervention, whereas the control group showed a decrease in VAS scores of 18.0% and 14.8%, respectively. In total, an average of 81.2% of participants administered the 2BCT had reported a statistically significant improvement from baseline to postintervention, compared with 22.9% of participants administered glucosamine and chondroitin.
CONCLUSIONS: In vivo studies confirmed that the bioactive proteins (Cyplexinol) within the 2BCT stimulated de novo bone and cartilage tissue production, demonstrating osteoinduction. The intervention group reported greater improvements in the psychometric evaluations that assessed joint comfort when compared with participants given the glucosamine and chondroitin. The results suggest that 2BCT may provide a novel and synergistic response to preserving joint homeostasis and improving quality of life.
Integr Med (Encinitas). 2016 Oct;15(5):34-44.
PMID: 27980494 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 43. |
A novel lecithin based delivery form of Boswellic acids (Casperome®) for the management of osteo-muscular pain: a registry study in young rugby players.
Franceschi F, Togni S, Belcaro G, Dugall M, Luzzi R, Ledda A, Pellegrini L, Eggenhoffner R, Giacomelli L
OBJECTIVE: Several experimental studies and clinical trials support the potential of Boswellia serrata extracts (BSE) for the treatment of various inflammatory diseases. The aim of this registry study was to assess the safety and the efficacy of a novel lecithin-based delivery form of Boswellia serrata extract (Casperome®) in the supportive management of osteo-muscular pain.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: 52 healthy young rugby players with acute knee pain and inflammation were recruited. Informed participants freely decided to follow either a standard management (SM) to control joint pain (control group = 27) or SM associated with oral daily supplementation with Casperome® (supplement group =25). Parameters associated with osteo-muscular pain and inflammation, and measurements of joint health and functions were assessed at the inclusion and after a 4-week supplementation.
RESULTS: A significant beneficial effect of Casperome® vs SM alone was observed for all the parameters evaluated, namely: local pain on effort; pain-free walking distance (treadmill test); minimal joint effusion; structural damage (joint, tendons, muscles) and intramuscular hematomas; thermal imaging of the anterior knee; Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain); need for concomitant drugs and medical attention; measurement of inflammatory biomarkers.
CONCLUSIONS: Our registry study suggests that Casperome® supplementation could represent an effective and safe, integrated approach for the treatment of osteo-muscular pain and inflammation.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Oct;20(19):4156-4161.
PMID: 27775780 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 44. |
Clinical comparison of oral administration and viscosupplementation of hyaluronic acid (HA) in early knee osteoarthritis.
Ricci M, Micheloni GM, Berti M, Perusi F, Sambugaro E, Vecchini E, Magnan B
PURPOSE: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a progressive, chronic and degenerative joint disease characterized by a loss of articular cartilage. Treatment of OA is largely palliative based on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids and injections of steroids. Regarding conservative treatment, intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid (HA) can play a role in early symptomatic knee OA.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Between August 2015 and September 2015, sixty patients (32 males and 28 females) between 40 and 70 years old were randomly allocated into two groups: Half were treated with three weekly intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid 1.6 % (group A), while the others were treated with Syalox 300 Plus (hyaluronic acid 300 mg + Boswellia serrata extract 100 mg) 1 tab/die for 20 days and afterward Syalox 150 (hyaluronic acid 150 mg) 1 tab/die for other 20 days (group B). All patients were evaluated clinically with American Knee Society Score (AKSS) and visual analogue scale (VAS) for the pain before the treatment and after 3 months.
RESULTS: AKSS of the patients in both groups was significantly increased by the treatment, and VAS score was significantly reduced. In both groups, two subgroups were created with patients older than 60 years and patients younger than 60 years. Better results are reported in younger patients of group A and older subjects in group B.
CONCLUSIONS: Despite several limitations, the results of the study have shown that HA injection and oral administration may have beneficial therapeutic effects on patients with early osteoarthritis. Different outcomes in younger and older subject suggested a combined therapy first with local infiltrations and then with oral composition.
Musculoskelet Surg. 2017 Apr;101(1):45-49.
PMID: 27681813 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 45. |
Nutraceutical supplement in the management of tendinopathies: a systematic review.
Fusini F, Bisicchia S, Bottegoni C, Gigante A, Zanchini F, Busilacchi A
BACKGROUND: nutraceuticals are common support therapy for management of tendinopathies. Even if they are widely diffused, our knowledge is still poor. The aim of this systematic review is to analyze the most commonly used nutraceuticals and their effects on tendons.
METHODS: glucosamine and chondroitin sulphate, vitamin C, hydrolazed type 1 collagen, arginine alpha-keto-glutarate, bromelain, curcumin, boswellic acid, and methil-sulfonil-methane were considered. During the last week of Dicember 2015 a comprehensive research of main databases for each substance was made in relation with tendinopathy. Repeated articles, articles not in English nor in Italian, not common nutraceuticals, and articles not related with tendons or tenocytes were excluded. Clinical article quality was assessed independently by two reviewers using the modified Coleman methodology score.
RESULTS: preclinical and clinical data from 46 articles from all databases were analyzed. All these nutraceuticals demonstrated several effects on normal and pathological tendons. Preclinical and clinical studies showed a possible role on collagen synthesis, inflammation, mechanical properties, and maturation of collagen bundles, antioxidant effect, edema, and analgesia. The majority clinical studies had some methodological limitations with an average Modified Coleman Methodology Score of 51.3 points and SD of 20.5 points. In particular, there were very low values in power, error, outcome assessment, and clinical effect.
CONCLUSION: preclinical results are very encouraging, however they are not fully confirmed by clinical studies. There are few clinical papers on the use of nutraceuticals in tendon disorders, and their methodological quality is poor. Furthermore, in most of the studies more than one supplement was administered at the same time. This may bias the results, and the effect of each single component cannot be determined. Furthermore, the interactions between nutraceuticals and drugs, or other dietary supplements (especially at high doses) has not been evaluated, neither their effects on chronic diseases. For these reasons, it is not possible to draw any definitive raccomendations on the use of nutraceutical supplementation in tendinopathies.
Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2016;6(1):48-57.
PMID: 27331031 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 46. |
Benefits of antioxidant supplements for knee osteoarthritis: rationale and reality.
Grover AK, Samson SE
Arthritis causes disability due to pain and inflammation in joints. There are many forms of arthritis, one of which is osteoarthritis whose prevalence increases with age. It occurs in various joints including hip, knee and hand with knee osteoarthritis being more prevalent. There is no cure for it. The management strategies include exercise, glucosamine plus chondroitin sulfate and NSAIDs. In vitro and animal studies provide a rationale for the use of antioxidant supplements for its management. This review assesses the reality of the benefits of antioxidant supplements in the management of knee osteoarthritis. Several difficulties were encountered in examining this issue: poorly conducted studies, a lack of uniformity in disease definition and diagnosis, and muddling of conclusions from attempts to isolate the efficacious molecules. The antioxidant supplements with most evidence for benefit for pain relief and function in knee osteoarthritis were based on curcumin and avocado-soya bean unsaponifiables. Boswellia and some herbs used in Ayurvedic and Chinese medicine may also be useful. The benefits of cuisines with the appropriate antioxidants should be assessed because they may be more economical and easier to incorporate into the lifestyle.
Nutr J. 2016 Jan;15():1.
PMID: 26728196 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 47. |
Methylsulfonylmethane and boswellic acids versus glucosamine sulfate in the treatment of knee arthritis: Randomized trial.
Notarnicola A, Maccagnano G, Moretti L, Pesce V, Tafuri S, Fiore A, Moretti B
Until now glucosamine sulfate (GS) has been the most widely used supplement and has been shown to be efficacious in the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA). Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) and boswellic acids (BA) are new effective supplements for the management of inflammation and joint degeneration, according to previous experimental studies. The aim of our study is to test the effectiveness of association of MSM and BA in comparison with GS in knee arthritis.In this prospective randomized clinical trial, MEBAGA (Methylsulfonylmethane and Boswellic Acids versus Glucosamine sulfate in the treatment of knee Arthritis), 120 participants affected by arthritis of the knee were randomly assigned to an experimental group (MB group) or a control group (GS group) treated for 60 days with 5 g of MSM and 7.2 mg of BA or with 1500 mg of GS daily, respectively. At the 2-month (T1) and 6-months (T2) follow-up , the efficacy of these two nutraceuticals was assessed using the visual analog pain scale (VAS) and the Lequesne Index (LI) for joint function, along with the use of anti-inflammatory drugs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and anti-cyclooxygenase-2).The repeated measures ANOVA analysis shows that for VAS, LI, and the use of anti-inflammatory drugs scores there are improvements due to the time in the two groups (respectively, F=26.0; P<0.0001; F=4.15; P=0.02; F=3.38; P=0.04), with a tendency to better values for the MB group at T2.On the basis of these preliminary data, we could support the efficacy of the MSM in association with BA in the treatment of OA. These results are consistent with the anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effects previously occurred in experimental studies. This new combination of integration (MSM and BS) has presented good results and satisfactory in comparison with GS, until now the cornerstone of the treatment of arthritis in according to guidelines.
Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2016 Mar;29(1):140-6.
PMID: 26684635 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 48. |
Hand 'stress' arthritis in young subjects: effects of Flexiqule (pharma-standard Boswellia extract). A preliminary case report.
Belcaro G, Feragalli B, Cornelli U, Dugall M
This case report (supplement registry study) evaluated subjects with painful 'stress' arthritis of the hand mainly localized at the joints. The patients received a suggestion to follow a rehabilitation plan (standard management; SM). A second group also used the same SM in association with the oral, pharma-standard supplement FlexiQule (Alchem) a new standardized, phytosomal preparation manufactured from the Boswellia plant, which can be used for self-management in inflammatory conditions (150 mg / 3 times daily). The two resulting registry groups included 12 subjects using SM+Flexiqule and and 11 controls (SM only). The groups were comparable. Serology showed no significant alterations: only ESR was slightly elevated (minimal elevation). After 2 weeks, the ESR was normal in the supplement group and mildly elevated in controls (p<0.05%). The decrease in hypertermic areas was greater/faster (p<0.05) in the supplement group. The identification of a working stress and the localization to the dominant hand was comparable in both groups. At 2 weeks, the decrease in pain was significantly faster and more important with the supplement (p<0.05). The hand became more usable in time and the score was better with the supplement (p<0.05). No supplemented patient had to use other drugs, while in the control group 3 subjects eventually used NSAIDs to control pain and stiffness and one used corticosteroids. In conclusion, the natural extract Flexiqule was effective in controlling work-related stress arthritis (without inflammaìtory signs) over a 2 weeks period, better than only Standard Management. More prolonged and larger studies are needed.
Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2015 Oct;():.
PMID: 26492590 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 49. |
Management of osteoarthritis (OA) with the pharma-standard supplement FlexiQule (Boswellia): a 12-week registry.
Belcaro G, Dugall M, Luzzi R, Ledda A, Pellegrini L, Hu S, Ippolito E
UNLABELLED: This registry study assessed the pharma-standard supplement FlexiQule (Boswellia extract in capsules) in the management of symptoms associated to osteoarthritis (OA) also managed with the 'standard management' (SM) in comparison with a group of patients managed only with SM. The 12- week registry included patients with symptomatic knee arthrosis. They were able to walk on a treadmill for a walking test and to complete the WOMAC questionnaire.
RESULTS: 32 patients used the supplement and 34 acted as controls (SM). No safety problems were observed. At 12 weeks, the Karnofsky scale was significantly improved in both groups: the variation was higher (p<0.05) in the supplement group. The WOMAC score was decreased significantly more in the supplement+SM group in comparison with controls considering pain, stiffness and physical functions (p<0.05). For social and emotional functions the decrease in score was also more evident in the supplement group (p<0.05). Both groups improved in pain-free and total walking distance at 12 weeks. Pain-free walking distance (treadmill) was higher (p<0.05) with the supplement (from 93.4;11.6 m to 271.3;19.3 m) than in controls (from 90.5;13.5 m to 158.3;22.3)(p<0.05). The improvement in total walking distance was also higher in the supplement group (p<0.05) (from 164.3;23.2 to 322.3;22.3 m) in comparison with the SM- only group ( from 158.3;18,4 to 240.2;19.3 m). The need for concomitant drugs and medical attention during the registry was reduced more in the supplement group (p<0.05). In conclusion the difference between SM and the Flexiqule+SM was in favor of the management with the supplement for all target measurements. The product is safe and well tolerated.
Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2015 Oct;():.
PMID: 26492586 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 50. |
Effect of Sri Lankan traditional medicine and Ayurveda on Sandhigata Vata (osteoarthritis of knee joint).
Perera PK, Perera M, Kumarasinghe N
Reported case was a 63-year-old female with end-stage osteoarthritis (OA) (Sandhigata Vata) of the left knee joint accompanied by exostoses. Radiology (X-ray) report confirmed it as a Kellgren-Lawrence grade III or less with exostoses. At the beginning, the Knee Society Rating System scores of pain, movement and stability were poor, and function score was fair. Srilankan traditional and Ayurveda medicine treatment was given in three regimens for 70 days. After 70 days, external treatment of oleation and 2 capsules of Shallaki (Boswellia serrata Triana and Planch) and two tablets of Jeewya (comprised of Emblica officinalis Gaertn., Tinospora cordifolia [Willd.] Millers. and Terminalia chebula Retz.), twice daily were continued over 5 months. Visual analogue scale for pain, knee scores in the Knee Society online rating system and a Ayurveda clinical assessment criteria was used to evaluate the effects of treatments in weekly basis. After treatment for 70 days, the Knee Society Rating System scores of pain, movement and stability were also improved up to good level and function score was improved up to excellent level. During the follow-up period, joint symptoms and signs and the knee scores were unchanged. In conclusion, this OA patient's quality of life was improved by the combined treatment of Sri Lankan traditional medicine and Ayurveda.
Ayu. 2014;35(4):411-5.
PMID: 26195904 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 51. |
FlexiQule (Boswellia extract) in the supplementary management of osteoarthritis: a supplement registry.
Belcaro G, Dugall M, Luzzi R, Ledda A, Pellegrini L, Cesarone MR, Hosoi M, Errichi M, Francis S, Cornelli U
UNLABELLED: The aim of the present pilot, registry study was an assessment in a supplement study of FlexiQule (standardized Boswellia extract) capsules in the supplementary management of patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis (OA) also treated with the "standard management" (SM) in comparison with a group of patients only managed with SM.
METHODS: This 4-week study included patients with symptomatic knee arthrosis (X-ray). Registry subjects were able to perform a treadmill walking test and to understand questions from the WOMAC questionnaire. Exclusion criteria were conditions requiring drug treatment, Body Mass Index >25, metabolic disorders, surgery within three months prior to inclusion, oncological condition or inability to walk.
RESULTS: Twenty-seven registry subjects using the supplement+SM and 28 using only SM completed the registry; at inclusion, the two groups were comparable including Karnofsky scale, WOMAC Score and the Treadmill Test. Of the subjects completing the registry 24 preferred to use the combination SM and the supplement. Safety evaluation: no problems - indicating the suspension of the supplementation ‑ were observed. Routine blood tests were normal at inclusion and did not significantly vary at 4 weeks. The Karnofski Scale at 4 weeks was improved in both groups: from 74.3;3.1 to 88.9;5.3 (P<0.05) in the Boswellia group in comparison with a variation from 75.3;5.2 to 79.4;3.3 (P<0.05) in the SM. The effects of the supplement were significantly higher (P<0.05). The WOMAC Score was decreased significantly more in the supplement+SM group in comparison with controls considering pain, stiffness and physical functions (P<0.05). Social/emotional functions improved better with the supplement (P<0.05). Both groups improved their walking distance at 4 weeks. The improvement was higher (P<0.05) in the Boswellia group. The need for other drugs or tests during the registry period was reduced more in the supplement group (P<0.05).
CONCLUSION: The difference between SM and the supplementation associated to SM was significant) in favor of the supplementation with Boswellia for all target measurements evaluated in the registry at 4 weeks.
Minerva Med. 2014 Dec;105(6 Suppl 2):9-16.
PMID: 26076376 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 52. |
Co-analgesic therapy for arthroscopic supraspinatus tendon repair pain using a dietary supplement containing Boswellia serrata and Curcuma longa: a prospective randomized placebo-controlled study.
Merolla G, Dellabiancia F, Ingardia A, Paladini P, Porcellini G
BACKGROUND: The cuff tendon that is most prone to full-thickness rotator cuff tears is the supraspinatus (SSP). Arthroscopic SSP repair ensures good to satisfactory mid- to long-term clinical outcomes. However, the intense postoperative pain reduces rehabilitation compliance and is cause of patient dissatisfaction. Many natural compounds act by inhibiting inflammatory pathways in a similar way to anti-inflammatory drugs
MATERIALS AND METHODS: This was a prospective randomized trial designed to assess the analgesic effect of a dietary supplement (DS) containing Boswellia serrata and Curcuma longa in a population of subjects with full-thickness SSP tendon tear treated by arthroscopy. Three weeks before surgery, patients were randomized to receive Tendisulfur(®) (group T) or a placebo (group P) for 2 months. The primary outcome measure was subjective VAS pain. Secondary outcomes measures were Constant-Murley score simple shoulder test, and patient global assessment (PGA) scores. Patients were assessed immediately at baseline and subsequently at 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 weeks.
RESULTS: Stratification of pain scores and subscores demonstrated significantly lower overall pain scores in group T versus group P at 1 week (p = 0.0477), and lower but not significantly different scores on week 2 (p = 0.0988); at subsequent time points, differences were not significant (p > 0.05). PGA scores were good in all subjects.
CONCLUSIONS: In conclusion, this study provides objective data on the effect of a DS containing natural substances, added to standard analgesics, on postoperative RC pain. DS alleviated short and partially mid-term pain, while long-term pain was unchanged. This limitation can probably be addressed by a dosage increase over the first 4 weeks and by extending treatment by 1 or 2 months.
Musculoskelet Surg. 2015 Sep;99 Suppl 1():S43-52.
PMID: 25957549 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 53. |
A medicinal herb-based natural health product improves the condition of a canine natural osteoarthritis model: a randomized placebo-controlled trial.
Moreau M, Lussier B, Pelletier JP, Martel-Pelletier J, Bédard C, Gauvin D, Troncy E
An oral herb-based natural health product (NHP) was evaluated in the canine natural osteoarthritis model. At baseline, the peak vertical force (PVF, primary endpoint) and case-specific outcome measure of disability (CSOM) were recorded in privately-owned dogs. Dogs (16/group) were randomized to receive NHP formulations or a negative control. The PVF was measured at week (W) 4 and W8. Daily locomotor activity was recorded using accelerometer. The CSOMs were assessed bi-weekly by the owner. The NHP-treated dogs (n = 13) had higher PVF at W4 (p = 0.020) and W8 (p <0.001) when compared to baseline. The changes at W8 were higher than control dogs (n = 14, p <0.027) and consistent with Cohen's d effect size of 0.7 (95% confidence interval: 0.0-1.5). The NHP-treated dogs had higher locomotor activity at W8 (p = 0.025) when compared to baseline. No significant change was observed for the CSOM. The NHP improved the clinical signs of osteoarthritis in this model.
Res Vet Sci. 2014 Dec;97(3):574-81.
PMID: 25311158 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 54. |
Oral herbal therapies for treating osteoarthritis.
Cameron M, Chrubasik S
BACKGROUND: Medicinal plant products are used orally for treating osteoarthritis. Although their mechanisms of action have not yet been elucidated in full detail, interactions with common inflammatory mediators provide a rationale for using them to treat osteoarthritic complaints.
OBJECTIVES: To update a previous Cochrane review to assess the benefits and harms of oral medicinal plant products in treating osteoarthritis.
SEARCH METHODS: We searched electronic databases (CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE, AMED, CINAHL, ISI Web of Science, World Health Organization Clinical Trials Registry Platform) to 29 August 2013, unrestricted by language, and the reference lists from retrieved trials.
SELECTION CRITERIA: Randomised controlled trials of orally consumed herbal interventions compared with placebo or active controls in people with osteoarthritis were included. Herbal interventions included any plant preparation but excluded homeopathy or aromatherapy products, or any preparation of synthetic origin.
DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS: Two authors used standard methods for trial selection and data extraction, and assessed the quality of the body of evidence using the GRADE approach for major outcomes (pain, function, radiographic joint changes, quality of life, withdrawals due to adverse events, total adverse events, and serious adverse events).
MAIN RESULTS: Forty-nine randomised controlled studies (33 interventions, 5980 participants) were included. Seventeen studies of confirmatory design (sample and effect sizes pre-specified) were mostly at moderate risk of bias. The remaining 32 studies of exploratory design were at higher risk of bias. Due to differing interventions, meta-analyses were restricted to Boswellia serrata (monoherbal) and avocado-soyabean unsaponifiables (ASU) (two herb combination) products.Five studies of three different extracts from Boswellia serrata were included. High-quality evidence from two studies (85 participants) indicated that 90 days treatment with 100 mg of enriched Boswellia serrata extract improved symptoms compared to placebo. Mean pain was 40 points on a 0 to 100 point VAS scale (0 is no pain) with placebo, enriched Boswellia serrata reduced pain by a mean of 17 points (95% confidence interval (CI) 8 to 26); number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) 2; the 95% CIs did not exclude a clinically significant reduction of 15 points in pain. Physical function was 33 points on the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) 0 to 100 point subscale (0 is no loss of function) with placebo, enriched Boswellia serrata improved function by 8 points (95% CI 2 to 14); NNTB 4. Assuming a minimal clinically important difference of 10 points, we cannot exclude a clinically important benefit in some people. Moderate-quality evidence (one study, 96 participants) indicated that adverse events were probably reduced with enriched Boswellia serrata (18/48 events versus 30/48 events with placebo; relative risk (RR) 0.60, 95% CI 0.39 to 0.92). Possible benefits of other Boswellia serrata extracts over placebo were confirmed in moderate-quality evidence from two studies (97 participants) of Boswellia serrata (enriched) 100 mg plus non-volatile oil, and low-quality evidence from small single studies of a 999 mg daily dose of Boswellia serrata extract and 250 mg daily dose of enrichedBoswellia serrata. It was uncertain if a 99 mg daily dose of Boswellia serrata offered benefits over valdecoxib due to the very low-quality evidence from a small single study. It was uncertain if there was an increased risk of adverse events or withdrawals with Boswellia serrata extract due to variable reporting of results across studies. The studies reported no serious adverse events. Quality of life and radiographic joint changes were not measured.Six studies examined the ASU product Piasclidine®. Moderate-quality evidence from four studies (651 participants) indicated that ASU 300 mg produced a small and clinically questionable improvement in symptoms, and probably no increased adverse events compared to placebo after three to 12 months treatment. Mean pain with placebo was 40.5 points on a VAS 0 to 100 scale (0 is no pain), ASU 300 mg reduced pain by a mean of 8.5 points (95% CI 1 to 16 points); NNTB 8. ASU 300 mg improved function (standardised mean difference (SMD) -0.42, 95% CI -0.73 to -0.11). Function was estimated as 47 mm (0 to 100 mm scale, where 0 is no loss of function) with placebo, ASU 300 mg improved function by a mean of 7 mm (95% CI 2 to 12 mm); NNTB 5 (3 to 19). There were no differences in adverse events (5 studies, 1050 participants) between ASU (53%) and placebo (51%) (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.97 to 1.12); withdrawals due to adverse events (1 study, 398 participants) between ASU (17%) and placebo (15%) (RR 1.14, 95% CI 0.73 to 1.80); or serious adverse events (1 study, 398 participants) between ASU (40%) and placebo (33%) (RR 1.22, 95% CI 0.94 to 1.59). Radiographic joint changes, measured as change in joint space width (JSW) in two studies (453 participants) did not differ between ASU 300 mg treatment (-0.53 mm) and placebo (-0.65 mm); mean difference of -0.12 (95% CI -0.43 to 0.19). Moderate-quality evidence from a single study (156 participants) confirmed possible benefits of ASU 600 mg over placebo, with no increased adverse events. Low-quality evidence (1 study, 357 participants) indicated there may be no differences in symptoms or adverse events between ASU 300 mg and chondroitin sulphate. Quality of life was not measured.All other herbal interventions were investigated in single studies, limiting conclusions. No serious side effects related to any plant product were reported.
AUTHORS' CONCLUSIONS: Evidence for the proprietary ASU product Piasclidine® in the treatment of osteoarthritis symptoms seems moderate to high for short term use, but studies over a longer term and against an apparently active control are less convincing. Several other medicinal plant products, including extracts of Boswellia serrata, show trends of benefits that warrant further investigation in light of the fact that the risk of adverse events appear low.There is no evidence that Piasclidine® significantly improves joint structure, and limited evidence that it prevents joint space narrowing. Structural changes were not tested for with any other herbal intervention.Further investigations are required to determine optimum daily doses producing clinical benefits without adverse events.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 May;2014(5):CD002947.
PMID: 24848732 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 55. |
A commercialized dietary supplement alleviates joint pain in community adults: a double-blind, placebo-controlled community trial.
Nieman DC, Shanely RA, Luo B, Dew D, Meaney MP, Sha W
BACKGROUND: The purpose of this study was to assess the effect of 8-weeks ingestion of a commercialized joint pain dietary supplement (Instaflex™ Joint Support, Direct Digital, Charlotte, NC) compared to placebo on joint pain, stiffness, and function in adults with self-reported joint pain. Instaflex™ is a joint pain supplement containing glucosamine sulfate, methylsufonlylmethane (MSM), white willow bark extract (15% salicin), ginger root concentrate, boswella serrata extract (65% boswellic acid), turmeric root extract, cayenne, and hyaluronic acid.
METHODS: Subjects included 100 men and women, ages 50-75 years, with a history (>3 months) of joint pain, and were randomized to Instaflex™ or placebo (3 colored gel capsules per day for 8 weeks, double-blind administration). Subjects agreed to avoid the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) and all other medications and supplements targeted for joint pain. Primary outcome measures were obtained pre- and post-study and included joint pain severity, stiffness, and function (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities [WOMAC]), and secondary outcome measures included health-related quality of life (Short Form 36 or SF-36), systemic inflammation (serum C-reactive protein and 9 plasma cytokines), and physical function (6-minute walk test). Joint pain symptom severity was assessed bi-weekly using a 12-point Likert visual scale (12-VS).
RESULTS: Joint pain severity was significantly reduced in Instaflex™ compared to placebo (8-week WOMAC, ↓37% versus ↓16%, respectively, interaction effect P = 0.025), with group differences using the 12-VS emerging by week 4 of the study (interaction effect, P = 0.0125). Improvements in ability to perform daily activities and stiffness scores in Instaflex™ compared to placebo were most evident for the 74% of subjects reporting knee pain (8-week WOMAC function score, ↓39% versus ↓14%, respectively, interaction effect P = 0.027; stiffness score, ↓30% versus ↓12%, respectively, interaction effect P = 0.081). Patterns of change in SF-36, systemic inflammation biomarkers, and the 6-minute walk test did not differ significantly between groups during the 8-week study
CONCLUSIONS: Results from this randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled community trial support the use of the Instaflex™ dietary supplement in alleviating joint pain severity in middle-aged and older adults, with mitigation of difficulty performing daily activities most apparent in subjects with knee pain.
Nutr J. 2013 Nov;12(1):154.
PMID: 24274358 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 56. |
Clinical evaluation of a formulation containing Curcuma longa and Boswellia serrata extracts in the management of knee osteoarthritis.
Kizhakkedath R
A formulation containing Curcuma longa and Boswellia serrata extracts (CB formulation) was evaluated for safety and efficacy in osteoarthritic patients and directly compared with the selective COX-2 inhibitor, celecoxib. In total, 54 subjects were screened, 30 subjects were enrolled and 28 completed the study. The treatment was well tolerated and did not produce any adverse effect in patients, as judged by the vital signs, hemogram, liver and renal function tests. The CB formulation at 500 mg administered twice a day, was more successful than administering celecoxib 100 mg twice a day for symptom scoring and clinical examination. The formulation was found to be safe and no dose-related toxicity was found.
Mol Med Rep. 2013 Nov;8(5):1542-8.
PMID: 24002213 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 57. |
Ayurvedic medicine offers a good alternative to glucosamine and celecoxib in the treatment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, controlled equivalence drug trial.
Chopra A, Saluja M, Tillu G, Sarmukkaddam S, Venugopalan A, Narsimulu G, Handa R, Sumantran V, Raut A, Bichile L, Joshi K, Patwardhan B
OBJECTIVE: To demonstrate clinical equivalence between two standardized Ayurveda (India) formulations (SGCG and SGC), glucosamine and celecoxib (NSAID).
METHODS: Ayurvedic formulations (extracts of Tinospora cordifolia, Zingiber officinale, Emblica officinalis, Boswellia serrata), glucosamine sulphate (2 g daily) and celecoxib (200 mg daily) were evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, parallel-efficacy, four-arm, multicentre equivalence drug trial of 24 weeks duration. A total of 440 eligible patients suffering from symptomatic knee OA were enrolled and monitored as per protocol. Primary efficacy variables were active body weight-bearing pain (visual analogue scale) and modified WOMAC pain and functional difficulty Likert score (for knee and hip); the corresponding a priori equivalence ranges were ±1.5 cm, ±2.5 and ±8.5.
RESULTS: Differences between the intervention arms for mean changes in primary efficacy variables were within the equivalence range by intent-to-treat and per protocol analysis. Twenty-six patients showed asymptomatic increased serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase (SGPT) with otherwise normal liver function; seven patients (Ayurvedic intervention) were withdrawn and SGPT normalized after stopping the drug. Other adverse events were mild and did not differ by intervention. Overall, 28% of patients withdrew from the study.
CONCLUSION: In this 6-month controlled study of knee OA, Ayurvedic formulations (especially SGCG) significantly reduced knee pain and improved knee function and were equivalent to glucosamine and celecoxib. The unexpected SGPT rise requires further safety assessment.
TRIAL REGISTRATION: Clinical Drug Trial Registry-India, www.ctri.nic.in, CTRI/2008/091/000063.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013 Aug;52(8):1408-17.
PMID: 23365148 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 58. |
Clinical evaluation of Boswellia serrata (Shallaki) resin in the management of Sandhivata (osteoarthritis).
Gupta PK, Samarakoon SM, Chandola HM, Ravishankar B
Sandhigata vata is described under Vatavyadhi in all Ayurvedic texts. Charaka was the first to describe separately "Sandhigata anila", but it was not included under 80 types of nanatmaja vatavyadhi. Osteoarthritis is the most common degenerative joint disease that begins asymptomatically in middle age with progressive symptoms in advancing age. Majority of people by the age 40 years may develop osteoarthritis, especially in weight bearing joints. Females are prone with 25% prevalence, whereas males have a prevalence of 16%. In the present study, 56 patients fulfilling the diagnostic criteria of Sandhigata vata, divided into two groups. Patients of first group were administered with 500 mg capsule of Shallaki, 6 g per day (in three divided doses) with lukewarm water (n=29) and the second group) capsule Shallaki as above along with local application of Shallaki ointment on the affected joints (n=23). After a course of therapy for 2 months, symptomatic improvement was observed in both the groups at various levels with promising results in the patients of first group.
Ayu. 2011 Oct;32(4):478-82.
PMID: 22661840 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 59. |
A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled clinical study evaluates the early efficacy of aflapin in subjects with osteoarthritis of knee.
Vishal AA, Mishra A, Raychaudhuri SP
Aflapin(®) is a novel synergistic composition derived from Boswellia serrata gum resin (Indian Patent Application No. 2229/CHE/2008). Aflapin is more efficacious as an anti-inflammatory agent compared to the existing Boswellia products, 5-Loxin(®) and traditional 65% Boswellia extract. A 30-day, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study was conducted to validate the efficacy of Aflapin(®) in the management of clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee (Clinical trial registration number: ISRCTN69643551). Sixty eligible OA subjects selected through screening were included in the study. The subjects received either 100 mg (n=30) of Aflapin(®) or placebo (n=30) daily for 30 days. Each subject was evaluated for pain and physical functions by using the standard tools (visual analog scale, Lequesne's Functional Index, and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index) at the baseline (day 0), and at days 5, 15 and 30. A series of biochemical tests in serum, urine and hematological parameters established the safety of Aflapin. The observations suggest that Aflapin conferred clinically and statistically significant improvements in pain scores and physical function scores in OA subjects. Aflapin provided significant improvements in pain score and functional ability in as early as 5 days of treatment. In conclusion, our observations suggest that Aflapin is a safe, fast acting and effective alternative intervention in the management of OA.
Int J Med Sci. 2011;8(7):615-22.
PMID: 22022214 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 60. |
The "MESACA" study: methylsulfonylmethane and boswellic acids in the treatment of gonarthrosis.
Notarnicola A, Tafuri S, Fusaro L, Moretti L, Pesce V, Moretti B
INTRODUCTION: Osteoarthritis is a chronic rheumatoid disease mediated by metalloproteinases and inflammatory cytokines. Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) and boswellic acids (BA) each show promise in the treatment of inflammatory processes, but the efficacy of combined treatment with these substances in the treatment of arthritis has not yet been studied.
METHODS: In this prospective randomized clinical trial, MESACA (for "methylsulfonylmethane and boswellic acids in the treatment of knee arthritis"), 60 subjects affected by arthritis of the knee were randomly assigned to an experimental group treated for 60 days with 5 g of MSM and 7.2 mg of BA daily, or a control group which was administered a placebo. At 2 and 6 months follow-up (FU), the efficacy of combined treatment with these two dietary supplements was assessed using the visual analog pain scale (VAS) and the Lequesne index (LI) for joint function, as well as monitoring the use of anti-inflammatory drugs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and anti-cyclooxygenase-2).
RESULTS: Pain, assessed with the VAS scale, was worse in the group treated with MSM and BA as compared with the placebo group at 2 months FU (3.8 vs. 2.7; P=0.04), whereas no difference between the two groups was observed at 6 months FU (2.7 vs. 3.6; P=0.2). No statistically significant differences were found in the LI between the two groups at either FU (2 months: 4.8 vs. 4.2; P=0.51; 6 months: 4.4 vs. 4.5; P=0.91). By contrast, a statistically significant difference in patients need for anti-inflammatory drugs was seen in the experimental as compared to the placebo group, even by 2 months FU (0.2 vs. 0.6 tablets/day; P<0.0001), that persisted up to the end of the study (0.1 vs. 0.6 tablets/day; P<0.0001).
CONCLUSIONS: Although the combined administration of MSM and BA in the treatment of gonarthrosis was not shown to be more efficacious than placebo in the management of the clinical and functional picture, it significantly reduced patients need for anti-inflammatory drugs.
Adv Ther. 2011 Oct;28(10):894-906.
PMID: 21986780 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 61. |
Antiarthritic activity of a standardized, multiherbal, Ayurvedic formulation containing Boswellia serrata: in vitro studies on knee cartilage from osteoarthritis patients.
Sumantran VN, Joshi AK, Boddul S, Koppikar SJ, Warude D, Patwardhan B, Chopra A, Chandwaskar R, Wagh UV
A validated in vitro model of cartilage damage and published data were used showing that this model measures the chondroprotective and antiinflammatory effects of different antiarthritic drugs. In this report, this model was used to evaluate the effects of a new antiarthritic Ayurvedic formulation containing Zingiber officinale root, Tinospora cordifolia stem, Phyllanthus emblica fruit and oleoresin of Boswellia serrata. Glucosamine sulphate was used as a positive control in the study. Aqueous extracts of each drug were tested on explant cultures of knee cartilage obtained from osteoarthritis patients undergoing knee replacement surgery. The new formulation caused a sustained and statistically significant inhibition in the release of glycosaminoglycans and aggrecan by cartilage explants from these patients. This formulation also induced a transient antiinflammatory effect as measured by a reduction in the levels of nitric oxide released by explants. Furthermore, the data strongly suggest that oleoresin of B. serrata plays a crucial role in the chondroprotective and antiinflammatory activity of this formulation. In summary, this report provides the first, direct, in vitro biochemical evidence of anti-arthritic activity a new Ayurvedic formulation. This formulation significantly reduced damage of articular knee cartilage from chronic osteoarthritis patients.
Phytother Res. 2011 Sep;25(9):1375-80.
PMID: 25363757 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 62. |
Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 5-Loxin and AflapinAgainst osteoarthritis of the knee: a double blind, randomized, placebo controlled clinical study.
Sengupta K, Krishnaraju AV, Vishal AA, Mishra A, Trimurtulu G, Sarma KV, Raychaudhuri SK, Raychaudhuri SP
Aflapin(®) is a novel synergistic composition derived from Boswellia serrata gum resin (Indian Patent Application No. 2229/CHE/2008). Aflapin is significantly better as an anti-inflammatory agent compared to the Boswellia extracts presently available in the market. A 90-day, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study was conducted to evaluate the comparative efficacy and tolerability of 5-Loxin(®) and Aflapin(®) in the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee (Clinical trial registration number: ISRCTN80793440). Sixty OA subjects were included in the study. The subjects received either 100 mg (n=20) of 5-Loxin(®) or 100 mg (n=20) of Aflapin(®) or a placebo (n=20) daily for 90 days. Each patient was evaluated for pain and physical functions by using the standard tools (visual analog scale, Lequesne's Functional Index, and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index) at the baseline (day 0), and at days 7, 30, 60 and 90. A battery of biochemical parameters in serum, urine and hematological parameters in citrated whole blood were performed to assess the safety of 5-Loxin(®) and Aflapin(®) in OA subjects. Fifty seven subjects completed the study. At the end of the study, both 5-Loxin(®) and Aflapin conferred clinically and statistically significant improvements in pain scores and physical function scores in OA subjects. Interestingly, significant improvements in pain score and functional ability were recorded as early as 7 days after initiation of the study in the treatment group supplemented with 100 mg Aflapin. Corroborating the improvements in pain scores in treatment groups, our in vitro studies provide evidences that Aflapin(®) is capable of inhibiting cartilage degrading enzyme MMP-3 and has the potential to regulate the inflammatory response by inhibiting ICAM-1. Aflapin(®) and 5-Loxin(®) reduce pain and improve physical functions significantly in OA subjects. Aflapin exhibited better efficacy compared to 5-Loxin(®). In comparison with placebo, the safety parameters were almost unchanged in the treatment groups. Hence both 5-Loxin(®) and Aflapin(®) are safe for human consumption.
Int J Med Sci. 2010 Nov;7(6):366-77.
PMID: 21060724 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 63. |
A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled study of the efficacy and safety of 5-Loxin for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee.
Sengupta K, Alluri KV, Satish AR, Mishra S, Golakoti T, Sarma KV, Dey D, Raychaudhuri SP
INTRODUCTION: 5-Loxin is a novel Boswellia serrata extract enriched with 30% 3-O-acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid (AKBA), which exhibits potential anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting the 5-lipoxygenase enzyme. A 90-day, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of 5-Loxin in the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee.
METHODS: Seventy-five OA patients were included in the study. The patients received either 100 mg (n = 25) or 250 mg (n = 25) of 5-Loxin daily or a placebo (n = 25) for 90 days. Each patient was evaluated for pain and physical functions by using the standard tools (visual analog scale, Lequesne's Functional Index, and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index) at the baseline (day 0), and at days 7, 30, 60 and 90. Additionally, the cartilage degrading enzyme matrix metalloproteinase-3 was also evaluated in synovial fluid from OA patients. Measurement of a battery of biochemical parameters in serum and haematological parameters, and urine analysis were performed to evaluate the safety of 5-Loxin in OA patients.
RESULTS: Seventy patients completed the study. At the end of the study, both doses of 5-Loxin conferred clinically and statistically significant improvements in pain scores and physical function scores in OA patients. Interestingly, significant improvements in pain score and functional ability were recorded in the treatment group supplemented with 250 mg 5-Loxin as early as 7 days after the start of treatment. Corroborating the improvements in pain scores in treatment groups, we also noted significant reduction in synovial fluid matrix metalloproteinase-3. In comparison with placebo, the safety parameters were almost unchanged in the treatment groups.
CONCLUSION: 5-Loxin reduces pain and improves physical functioning significantly in OA patients; and it is safe for human consumption. 5-Loxin may exert its beneficial effects by controlling inflammatory responses through reducing proinflammatory modulators, and it may improve joint health by reducing the enzymatic degradation of cartilage in OA patients.
TRIAL REGISTRATION: (
CLINICAL TRIAL REGISTRATION NUMBER: ISRCTN05212803.).
Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(4):R85.
PMID: 18667054 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 64. |
Nutraceuticals in the management of osteoarthritis.
Clayton JJ
Orthopedics. 2007 Aug;30(8):624-9; quiz 630-1.
PMID: 17727018 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 65. |
Natural products as a gold mine for arthritis treatment.
Khanna D, Sethi G, Ahn KS, Pandey MK, Kunnumakkara AB, Sung B, Aggarwal A, Aggarwal BB
Arthritis, an inflammation of the joints, is usually a chronic disease that results from dysregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g. tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-1beta) and pro-inflammatory enzymes that mediate the production of prostaglandins (e.g. cyclooxygenase-2) and leukotrienes (e.g. lipooxygenase), together with the expression of adhesion molecules and matrix metalloproteinases, and hyperproliferation of synovial fibroblasts. All of these factors are regulated by the activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB. Thus, agents that suppress the expression of tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1beta, cyclooxygenase-2, lipooxygenase, matrix metalloproteinases or adhesion molecules, or suppress the activation of NF-kappaB, all have potential for the treatment of arthritis. Numerous agents derived from plants can suppress these cell signaling intermediates, including curcumin (from turmeric), resveratrol (red grapes, cranberries and peanuts), tea polyphenols, genistein (soy), quercetin (onions), silymarin (artichoke), guggulsterone (guggul), boswellic acid (salai guggul) and withanolides (ashwagandha). Indeed, several preclinical and clinical studies suggest that these agents have potential for arthritis treatment. Although gold compounds are no longer employed for the treatment of arthritis, the large number of inexpensive natural products that can modulate inflammatory responses, but lack side effects, constitute 'goldmines' for the treatment of arthritis.
Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2007 Jun;7(3):344-51.
PMID: 17475558 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 66. |
Evidence of effectiveness of herbal antiinflammatory drugs in the treatment of painful osteoarthritis and chronic low back pain.
Chrubasik JE, Roufogalis BD, Chrubasik S
Treatment with herbal medicines is very popular in Europe. In order to get information on the evidence of effectiveness of oral herbal medicines in the treatment of pain in the joints or lower back, OVID(MEDLINE), PUBMED and COCHRANE COLLABORATION LIBRARY were searched back to 1985 for systematic reviews. The level of evidence of effectiveness was defined as strong - at least two confirmatory studies demonstrating a clinical relevant effect, moderate - one confirmatory study with a clinical relevant effect and/or multiple exploratory studies of good quality; otherwise the evidence was insufficient or conflicting in the case of inconsistent findings. Fifteen systematic reviews were identified. The evidence of effectiveness was strong for a proprietary unsaponifiable avocado soybean fraction and Harpagophytum preparations containing > 50 mg harpagoside in the daily dosage, moderate for ginger and a proprietary rose hip and seed powder, insufficient for Boswellia serrata gum resin and other herbal preparations and inconsistent for a proprietary willow bark extract. Further rigorous studies are required to confirm the usefulness of herbal medicines in the treatment of osteoarthritic complaints and chronic low back pain in order to enable acceptance of the herbal medicines into the treatment guidelines.
Phytother Res. 2007 Jul;21(7):675-83.
PMID: 17444576 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 67. |
A 32-week randomized, placebo-controlled clinical evaluation of RA-11, an Ayurvedic drug, on osteoarthritis of the knees.
Chopra A, Lavin P, Patwardhan B, Chitre D
BACKGROUND: The ancient Indian (Asian) Ayurvedic medicinal system uses herbomineral drugs to treat arthritis. Despite centuries of use, very few have been tested by drug trials. RA-11 (ARTREX, MENDAR), a standardized multiplant Ayurvedic drug (Withania somnifera, Boswellia serrata, Zingiber officinale, and Curcuma longa) is currently used to treat arthritis.
OBJECTIVE: The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of RA-11 in patients with symptomatic osteoarthritis (OA) of the knees.
METHODS: A total of 358 patients with chronic knee pain were screened free-of-cost in "arthritis camps" in an Indian metropolis. Ninety patients with primary OA of the knees (ACR classification; Arthritis Rheum 1986;29:1039-1049) were found eligible (postanalgesic washout pain visual analog score [VAS] > or =40 mm in either or both knees on body weight-bearing activities) to enroll into a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel efficacy, single-center, 32-week drug trial (80% power to detect 25% difference, P = 0.05, 2-sided). Concurrent analgesics/nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and steroids in any form were not allowed. Lifestyle and/or dietary restrictions, as per routine Ayurveda practices, were not imposed. Pain VAS (maximum pain in each knee recorded by the patient during the preceding 48 hours) and modified WOMAC (Western Ontario McMaster University OA Index, Likert scale, version 3.0) were the primary efficacy variables. The WOMAC section on "physical function difficulty" was modified for Indian use and validated before the trial. Routine laboratory testing was primarily done to monitor drug safety. At baseline, the groups (active = 45, placebo = 45) were well matched for several measures (mean pain VAS: active = 6.17; placebo = 6.5).
RESULTS: 1) EFFICACY: Compared with placebo, the mean reduction in pain VAS at week 16 (active = 2.7, placebo = 1.3) and week 32 (active = 2.8, placebo = 1.8) in the active group was significantly (P <0.05, analysis of variance [ANOVA]) better. Similarly, the improvement in the WOMAC scores at week 16 and week 32 were also significantly superior (P <0.01, ANOVA) in the active group. 2) SAFETY: Both the groups reported mild adverse events (AE) without any significant difference. 3) Withdrawals: Twenty-eight patients were discontinued. None reported drug-related toxicity. The majority failed follow up/compliance. No differences were observed between the groups.
CONCLUSION: This controlled drug trial demonstrates the potential efficacy and safety of RA- 11 in the symptomatic treatment of OA knees over 32 weeks of therapy.
J Clin Rheumatol. 2004 Oct;10(5):236-45.
PMID: 17043520 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 68. |
Dietary support with Boswellia resin in canine inflammatory joint and spinal disease.
Reichling J, Schmökel H, Fitzi J, Bucher S, Saller R
An open multi-centre veterinary clinical trial, comparing conditions before and after treatment with a herbal dietary supplement consisting of a natural resin extract of Boswellia serrata, was conducted by 10 practicing veterinarians in Switzerland. This traditional plant-based supplement is known for its anti-rheumatic and anti-inflammatory properties. 29 dogs with manifestations of chronic joint and spinal disease were enrolled. Osteoarthritis and degenerative conditions were confirmed radiologically in 25 of 29 cases. The resin extract (BSB108, product of Bogar AG) was administered with the regular food at a dose of 400 mg/10 kg body weight once daily for 6 weeks. Already after two weeks of treatment, an overall efficacy of the dietary supplement was evident in 71% of 24 eligible dogs. A statistically significant reduction of severity and resolution of typical clinical signs in individual animals, such as intermittent lameness, local pain and stiff gait, were reported after 6 weeks. Effects of external factors that aggravate lameness, such as "lameness when moving" and "lameness after a long rest" diminished gradually. In 5 dogs, reversible brief episodes of diarrhea and flatulence occurred, but only once was a relationship to the study preparation suspected. Because quality and stability of the resin extract were ensured, these data suggest that a standardized preparation can be recommended as a herbal dietary supplement providing symptomatic support in canine osteoarthritic disease.
Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 2004 Feb;146(2):71-9.
PMID: 14994484 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 69. |
Efficacy and tolerability of Boswellia serrata extract in treatment of osteoarthritis of knee--a randomized double blind placebo controlled trial.
Kimmatkar N, Thawani V, Hingorani L, Khiyani R
Osteoarthritis is a common, chronic, progressive, skeletal, degenerative disorder, which commonly affects the knee joint. Boswellia serrata tree is commonly found in India. The therapeutic value of its gum (guggulu) has been known. It posses good anti-inflammatory, anti-arthritic and analgesic activity. A randomized double blind placebo controlled crossover study was conducted to assess the efficacy, safety and tolerability of Boswellia serrata Extract (BSE) in 30 patients of osteoarthritis of knee, 15 each receiving active drug or placebo for eight weeks. After the first intervention, washout was given and then the groups were crossed over to receive the opposite intervention for eight weeks. All patients receiving drug treatment reported decrease in knee pain, increased knee flexion and increased walking distance. The frequency of swelling in the knee joint was decreased. Radiologically there was no change. The observed differences between drug treated and placebo being statistically significant, are clinically relevant. BSE was well tolerated by the subjects except for minor gastrointestinal ADRs. BSE is recommended in the patients of osteoarthritis of the knee with possible therapeutic use in other arthritis.
Phytomedicine. 2003 Jan;10(1):3-7.
PMID: 12622457 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 70. |
[Is H15 (resin extract of Boswellia serrata, "incense") a useful supplement to established drug therapy of chronic polyarthritis? Results of a double-blind pilot study].
Sander O, Herborn G, Rau R
BACKGROUND: Leukotrienes and prostaglandines are important mediators of inflammation. While prostaglandine synthesis can be influenced by NSAIDs therapeutical approaches to the 5-lipoxygenase pathway are rare. Resinous extracts of Boswellia serrata (H15, indish incense), known from traditional ayurvedic medicine, decrease leukotriene synthesis in vitro. Case reports suggest a clinical role for that drug.
METHODS: Outpatients with active RA have been enrolled into a multicenter controlled trial. Patients received 9 tablets of active drug (3600 mg) or placebo daily in addition to their previous therapy. Doses of NSAIDs could be adjusted on demand. Efficacy parameters, Ritchies Index for swelling and pain, ESR, CRP, pain on VAS and NSAID dose were documented at baseline and 6 and 12 weeks after initiation. Mean values and medians were calculated to compare the groups for significant or clinically relevant change from baseline or difference between both groups at any time point of observation.
RESULTS: A total of 78 patients were recruited in 4 centers, the data have been published in abstract form. Only 37 patients (verum 18, placebo 19), enrolled in Ratingen were available for detailed efficacy and safety analysis. All evaluations in these patients were performed by one investigator (G.H.). There was no subjective, clinical or laboratory parameter showing a significant or clinically relevant change from baseline or difference between both groups at any time point of observation. The mean NSAID dose reduction reached levels of 5.8% (H15) and 3.1% (placebo). One patient in each group showed a good response in all parameters but 4 patients in each group worsened. The others showed no alteration of their disease.
CONCLUSION: Treatment with H15 showed no measurable efficacy. Controlled studies including a greater patient population are necessary to confirm or reject our results.
Z Rheumatol. 1998 Feb;57(1):11-6.
PMID: 9566100 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 71. |
Special extract of BOSWELLIA serrata (H 15) in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Etzel R
H15, a special extract of the gum resin of Boswellia serrata (BS) is effective in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These findings were obtained in more than 260 patients by using a range of different clinical approaches for evaluation. The criteria for assessment were mainly joint swelling, pain, erytrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), stiffness, additional use of NSAID, side effects and tolerance. The therapeutic action was mainly proven by comparing H15 with a placebo standard therapy. H15 is:
Phytomedicine. 1996 May;3(1):91-4.
PMID: 23194870 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 72. |
Treatment of osteoarthritis with a herbomineral formulation: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study.
Kulkarni RR, Patki PS, Jog VP, Gandage SG, Patwardhan B
The clinical efficacy of a herbomineral formulation containing roots of Withania somnifera, the stem of Boswellia serrata, rhizomes of Curcuma longa and a zinc complex (Articulin-F), was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, cross-over study in patients with osteoarthritis. After a one-month single blind run-in period, 42 patients with osteoarthritis were randomly allocated to receive either a drug treatment or a matching placebo for a period of three months. After a 15-day wash-out period the patients were transferred to the other treatment for a further period of three months. Clinical efficacy was evaluated every fortnight on the basis of severity of pain, morning stiffness, Ritchie articular index, joint score, disability score and grip strength. Other parameters like erythrocyte sedimentation rate and radiological examination were carried out on a monthly basis. Treatment with the herbomineral formulation produced a significant drop in severity of pain (P less than 0.001) and disability score (P less than 0.05). Radiological assessment, however, did not show any significant changes in both the groups. Side effects observed with this formulation did not necessitate withdrawal of treatment.
J Ethnopharmacol. 1991;33(1-2):91-5.
PMID: 1943180 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|