Wie im experimentellen Teil gezeigt, hemmen gewissen Boswelliasäuren das Wachstum verschiedener Karzinomzellen in vitro durch
Studien, die eine Wirksamkeit eines Weihrauchextraktes oder von Boswelliasäuren beim Menschen beweisen, gibt es derzeit nicht.
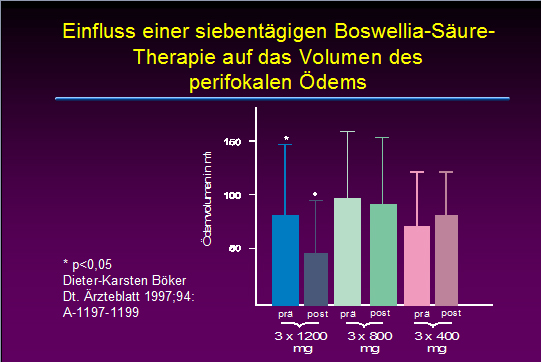
Dagegen gibt es einige Studien, die eine Verminderung peritumoraler Hirnödeme nahelegen. Dies könnte etwas mit der ödemproduzierenden Wirkung von Leukotrien zu tun haben, über die manche Tumore verfügen.
| 1. |
Integrative cancer treatment may have a survival benefit in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective cohort study from an integrative cancer center in Korea.
Bae K, Kim E, Kong JS, Kim J, Park SJ, Jun HJ, Cho CK, Kim MK, Yoo HS
Integrative oncology is being increasingly adopted in mainstream cancer care to strengthen anticancer effects and to control cancer-related symptoms.The objective of this study is to identify the characteristics of patients with lung cancer treated at an integrative cancer center in Korea and to determine the effects of integrative cancer treatment (ICT) on survival outcome in traditional Korean medicine (TKM).We reviewed medical records for lung cancer patients who visited a single integrative clinical setting, East-West Cancer Center, between January 2014 and December 2015. We classified the patients into groups according to their ICT and whether or not they underwent anticancer traditional Korean Medicine treatment with a multiherbal formula containing Panax notoginseng Radix, Cordyceps militaris, P ginseng C.A.Mey., and Boswellia carterii BIRDWOOD (HangAmDan-B), with a herbal formula containing Rhus verniciflua Stoke, or with cultivated wild ginseng pharmacopuncture. A descriptive analysis of the characteristics and a survival analysis using the Kaplan-Meier curves with log rank test and a Cox proportional hazard model were performed.A total of 91 patients were included, and the majority had advanced-stage cancer. Of those patients, 45.1% were in the mono-TKM group and 39.6% were integrative group. Patients with advanced stage had significantly higher mortality than patients with early stage (crude hazard ratio [HR]: 4.41, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.56-12.5; adjusted HR: 6.31, 95% CI: 1.24-32.1). In the unadjusted model, for patients in the integrative group, the mortality rate was reduced by 50% compared to mono-TKM group with statistical significance. After adjusting confounders, the mortality rate of integrative group was reduced by 6% compared to mono-TKM group, suggesting positive effect on survival probability of integrative group.The results suggest that integration of TKM and conventional cancer treatment may have survival benefits in patients with lung cancer. Even though this study has limitations including heterogeneity between treatment groups, the study results suggest that ICT has positive effect on survival probability. To clarify the impacts of ICT for lung cancer and other cancers on survival outcome, further prospective study with a rigorous study design is required in multiclinical setting.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jun;98(26):e16048.
PMID: 31261510 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 2. |
A novel lecithin-based delivery form of Boswellic acids as complementary treatment of radiochemotherapy-induced cerebral edema in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: a longitudinal pilot experience.
Di Pierro F, Simonetti G, Petruzzi A, Bertuccioli A, Botta L, Bruzzone MG, Cuccarini V, Fariselli L, Lamperti E
BACKGROUND: Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is an extremely challenging neurological disease for which the development of more effective therapeutic options and of adjuvant/complementary treatment is needed. We investigated the effects of an innovative phytosome-based delivery form of boswellic acids extract (Monoselect AKBA™) on radiochemotherapy-induced cerebral edema in patients with primary GBM.
METHODS: Patients with de novo GBM treated with surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy with temozolomide were enrolled in this longitudinal study and received boswellia-based product 4500 mg/die for a maximum of 34 weeks. Cerebral edema was assessed at 4, 12, 22 and 34 weeks post-surgery, together with steroids consumption and patients' psychological status.
RESULTS: A total of 20 patients were included in the study. The percentage of patients with reduced edema was constant during the study, while the percentage of those with reduced or stable edema tended to increase over time. Of note, two patients achieved a considerable reduction in brain edema, which led to a more favorable and beneficial surgical resection. In addition, a good percentage of patients assumed a stable/reduced steroids dose or were dexamethasone free during the study. Lastly, patients' QoL and psychological state were maintained throughout the study.
CONCLUSIONS: Complementary treatment with Monoselect AKBA™ might exert a beneficial effect in reducing radiochemotherapy-induced cerebral edema, thanks to the anti-inflammatory properties of the boswellia serrata extract. The reduction in brain edema might diminish dexamethasone assumption, thus minimizing steroids-induced side effects, and in few cases may allow a complete surgical excision of the tumor mass.
J Neurosurg Sci. 2019 Jun;63(3):286-291.
PMID: 31096725 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 3. |
Frankincense Essential Oil as a Supportive Therapy for Cancer-Related Fatigue: A Case Study.
Reis D, Jones TT
Fatigue experienced by patients diagnosed with cancer can be debilitating and can be challenging to manage. The use of supportive therapies such as essential oils is gaining popularity among patients diagnosed with cancer. This article describes one patient's experience using frankincense (Boswellia carterii) essential oil to help in the management of her fatigue. The topical application of the frankincense helped to take her fatigue from being barely able to lift her head to being able to do some basic activities of daily living.
Holist Nurs Pract. 2018 May/Jun;32(3):140-142.
PMID: 29642127 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 4. |
A Pilot Study to Examine the Effects of an Anti-inflammatory Supplement on Eicosanoid Derivatives in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease.
Shelmadine BD, Bowden RG, Moreillon JJ, Cooke MB, Yang P, Deike E, Griggs JO, Wilson RL
BACKGROUND: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a progressive disease with an inverse relationship between kidney function and levels of inflammation and oxidative stress. Curcumin and Boswellia serrata have been reported to exert anti-inflammatory effects on the cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase pathways. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to study the effects of a supplement containing curcumin and B. serrata on eicosanoid derivatives in early stage CKD patients who had not initiated hemodialysis.
METHODS: Sixteen patients with stage 2 and stage 3 CKD (56.0 ± 16.0 years, 171.4 ± 11.9 cm, 99.3 ± 20.2 kg) were randomized into a treatment group with curcumin and B. serrata or a placebo group. The dependent variables prostaglandin E (PGE), 5-hydroxyicosatetraenoic acid, 12-hydroxyicosatetraenoic acid, 15-hydroxyicosatetraenoic acid, and 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid were measured both before and after 8 weeks of supplementation. Results were analyzed by using a repeated-measures analysis of covariance for compliance and body-mass index.
RESULTS: A significant group effect (p = 0.05), and a trend for Group × Time interaction (p = 0.056) were detected for PGE. No significant differences were observed for any other variables.
CONCLUSIONS: This is the first article of baseline levels of the dependent variables in early stage CKD, and the first article to show a significant effect of these supplements on PGE in early stage CKD. Further studies are needed to determine whether curcumin and B. serrata may be effective means to reduce inflammation in patients with CKD.
J Altern Complement Med. 2017 Aug;23(8):632-638.
PMID: 28375641 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 5. |
Cancer Chemopreventive Effects of Boswellia sacra Gum Resin Hydrodistillates on Invasive Urothelial Cell Carcinoma: Report of a Case.
Xia D, Lou W, Fung KM, Wolley CL, Suhail MM, Lin HK
A 52-year-old Hispanic male presented with hematuria and was later diagnosed with a large invasive high-grade urothelial cell carcinoma (UCC) of the urinary bladder, but with ambiguous pT1/pT2 staging regarding musclaris propria invasion by UCC. The conventional treatment including radical cystoprostatectomy followed by neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without radiation therapy was presented. The patient decided to delay the standard therapy until a later stage, but elected to go through transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) without Bacillus Calmette-Guérin instillation. Following TURBT, the patient started oral Boswellia sacra gum resin (aka frankincense or Ru Xiang in Chinese) hydrodistillates (BSGRH) administration at 3 mL daily with lifestyle changes, and continued this regimen in the last 25 months. Within the first year after diagnosis, the patient experienced 2 recurrences. Recurrent tumors were removed by TURBT alone and both tumors were far smaller than the original one. After the second recurrence, the patient has no detectible cancer in the bladder based on cystoscopy for 14 months and has an intact genitourinary system. His liver and kidney functions are considered to be normal based on blood chemistry tests. This index case suggests that BSGRH may have cancer chemopreventive effects on UCC. The use of Boswellia-derived products in the management of cancer has been well document in other published studies, and boswellic acids have been suggested to be the major component. However, BSGRH contains very little boswellic acids. Demonstration of cancer chemoprevention using BSGRH is one step forward in isolating the key components other than boswellic acids in frankincense. The critical question as to whether these components can simultaneously activate multiple pathways in cancer cells to execute cancer suppression/cytotoxicity or prevention effects remains to be addressed. More studies including identification of key molecules, pharmacokinetics of major compounds, as well as long-term benefits and possible adverse effects will be needed to meet the guidelines of the US Food and Drug Administration for botanical drug development.
Integr Cancer Ther. 2017 12;16(4):605-611.
PMID: 27531547 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 6. |
A randomized trial of Boswellia in association with betaine and myo-inositol in the management of breast fibroadenomas.
Pasta V, Dinicola S, Giuliani A, Harrath AH, Alwasel SH, Tartaglia F, Cucina A, Bizzarri M
OBJECTIVE: Breast fibroadenoma is a common finding in young women and actually accounts for the majority of benign breast lumps. Fibroadenoma does not require any treatment unless clinical symptoms (mostly mastalgia) or histological markers of cancer risk (atypia) impose specific medical or surgical intervention. In symptomatic fibroadenoma, anti-estrogenic treatments provided evidence of success. Yet, these therapies are often associated with relevant side effects that lead to drug treatment discontinuation. Additionally, in such cases, relapse is a frequent issue. Therefore, an optimal strategy is still warranted. Boswellia, betaine and myo-inositol have already been proved to modulate different pathways - inflammatory, metabolic, oxidative and endocrine processes - in a wide array of human tissues. Based on that background, we hypothesized that these substances can effectively synergize in inducing the regression of fibroadenoma.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: We included 64 patients ≤ 30 years of age with fibroadenoma. The patients were randomized into two groups. The experimental group was treated with an association of Boswellia, betaine, myo-inositol, B-group vitamins and N-acetylcysteine for 6 months; otherwise, the placebo group was treated only with B-group vitamins and N-acetylcysteine. Patients were monitored at the enrollment and the end of the study for evaluating the clinical response.
RESULTS: A significant clinical improvement was observed in the experimental arm. Fibroadenoma median volume reduction averaged 17.86% in the experimental group and 5.96% in the placebo group. Moreover, 14 out of 36 (38.88%) patients showed a reduction of fibroadenoma volume compared to 5/28 (17.85%) observed in the placebo group (p = 0.005).
CONCLUSIONS: A supplementation with Boswellia, betaine and myo-inositol reduces fibroadenoma dimension in young women. No relevant side effects have been recorded.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016 05;20(9):1860-5.
PMID: 27212181 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 7. |
A Randomized Pilot Study of Inositol in Association with Betaine and Boswellia in the Management of Mastalgia and Benign Breast Lump in Premenopausal Women.
Pasta V, Dinicola S, Giuliani A, Harrath AH, Alwasel SH, Tartaglia F, Cucina A, Bizzarri M
Benign mammary lumps and mastalgia are the most common breast disorders; yet, there is no clear-cut consensus about the best strategy for their treatment. We hypothesized that a combination, including boswellic acid, betaine, and myoinositol, would be beneficial in breast disorders by exerting a pleiotropic effect on multiple pathways. Indeed, myoinositol has already been proven to modulate some factors involved in the genesis of breast diseases, such as fibrosis and metabolic and endocrine cues. In our study, 76 women were randomly assigned to either the experimental or the placebo arm. After six months of treatment, statistically significant differences between the two groups were recorded for pain relief (56% vs 17%) and breast density reduction (60% vs 9%). Furthermore, benign breast mass dimension showed a reduction in the experimental group (40% vs 16%). The combination of boswellic acid, betaine, and myoinositol has been demonstrated to be effective in the treatment of breast pain and radiologically and histologically confirmed benign breast mass and in the reduction of breast density, one of the pivotal risk factors for the development of breast cancer, without any side effects.
Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2016;10():37-43.
PMID: 27127407 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 8. |
An association of boswellia, betaine and myo-inositol (Eumastós) in the treatment of mammographic breast density: a randomized, double-blind study.
Pasta V, Gullo G, Giuliani A, Harrath AH, Alwasel SH, Tartaglia F, Cucina A, Bizzarri M
OBJECTIVE: Mammographic breast density is a recognized risk factor for breast cancer. The causes that lead to the proliferation of the glandular breast tissue and, therefore, to an increase of breast density are still unclear. However, a treatment strategy to reduce the mammary density may bring about very relevant clinical outcomes in breast cancer prevention. Myo-inositol is a six-fold alcohol of cyclohexane, has already been proved to modulate different pathways: inflammatory, metabolic, oxidative and endocrine processes, in a wide array of human diseases, including cancer and the genesis of mammary gland and breast diseases, like fibrosis, as well as metabolic and endocrine cues. Similarly, boswellic acid and betaine (three-methyl glycine) both inhibit inflammation and exert protective effects on breast physiology. Based on this scientific background, we hypothesized that a combination including, boswellic acid, betaine and myo-inositol would be able to reduce breast density working on different pathways.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: In this study, seventy-six premenopausal women were randomly assigned to the placebo and the experimental drug arms (Eumastós) for six months.
RESULTS: After 6 months of treatment, statistically significant difference between the two groups was recorded on the breast density reduction (60% vs. 9%), using mammographic as well as ultrasound examination.
CONCLUSIONS: Preliminary data collected here with support the starting assumptions, that the association comprising boswellic acid, betaine and myo-inositol significantly reduces mammary density, providing the first evidence for a new and safe approach for the management of mammographic density treatment.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Nov;19(22):4419-26.
PMID: 26636532 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 9. |
Clinical evaluation of safety and efficacy of Boswellia-based cream for prevention of adjuvant radiotherapy skin damage in mammary carcinoma: a randomized placebo controlled trial.
Togni S, Maramaldi G, Bonetta A, Giacomelli L, Di Pierro F
OBJECTIVE: Acute radiation erythema and other skin reactions are common adverse effects experienced by breast carcinoma patients undergoing radiotherapy treatment. Boswellic acids are pentacyclic triterpenes extracted from the resins of the tropical tree Boswellia serrata with strong anti-inflammatory properties. This study was designed to evaluate the safety and the efficacy of the application of a base cream containing boswellic acids in a proprietary formulation (Bosexil(R)) for the prevention and relief of radiation-induced adverse effects in breast cancer patients.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: The acute skin reactions were clinically evaluated by visual intensity and computer-assisted skin color analysis, and toxicity was assessed by the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) rating scale.
RESULTS: These findings indicate that the use of a boswellia-based cream is effective in reducing the use of topical corticosteroids and is able to reduce the grade of erythema and the skin superficial symptoms, being well tolerated by the patients.
CONCLUSIONS: Further studies comparing boswellia cream with other topical agents will be appropriate to confirm the effectiveness of this treatment for breast cancer patients under radiation therapy.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Apr;19(8):1338-44.
PMID: 25967706 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 10. |
The use of aromasticks at a cancer centre: a retrospective audit.
Dyer J, Cleary L, Ragsdale-Lowe M, McNeill S, Osland C
AIM: To consider the use of aromasticks in a cancer centre in the UK: the reasons for their use, the choice of essential oils used in them and the demographics of the patients to whom they were given.
BACKGROUND: Aromasticks are personal aromatherapy inhaler devices, used in this hospital by the complementary therapy team to improve patients' well-being and quality of life by helping with symptom control.
DESIGN: A retrospective audit of aromastick use covering a 28 month period from January 2011-April 2013.
RESULTS: A total of 514 aromasticks were given out, to patients with a variety of cancer diagnoses and symptoms. The most common reasons for aromastick use were to alleviate nausea or to encourage relaxation. Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia), lemon (Citrus limon), frankincense (Boswellia carterii), bergamot (Citrus bergamia), orange sweet (Citrus sinensis) and peppermint (Mentha x piperita) were the essential oils used most often.
Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2014 Nov;20(4):203-6.
PMID: 25486854 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 11. |
A case of metastatic bladder cancer in both lungs treated with korean medicine therapy alone.
Lee DH, Kim SS, Seong S, Woo CR, Han JB
This case report is aimed to investigate the effects of Korean medicine therapy (KMT) including oral herbal medicine and herb nebulizer therapy in treating metastatic bladder cancer in the lungs. A 74-year-old man was diagnosed with metastatic bladder cancer in both lungs in August 2013. He refused any chemotherapy and was admitted to our hospital in a much progressed state on January 11, 2014. Since then, he was treated with KMT until May 17, 2014. The main oral herbal medicines were Hyunamdan made of heat-processed ginseng, Hangamdan S made of Cordyceps militaris, Panax ginseng radix, Commiphora myrrha, calculus bovis, margarita, Boswellia carteri, Panax notoginseng radix and Cremastra appendiculata tuber, and nebulizer therapy with Soram nebulizer solution made of wild ginseng and Cordyceps sinensis distillate. Their effect was evaluated considering the change of the main symptoms and using serial chest X-ray. The size and number of multiple metastatic nodules in both lungs were markedly decreased and the symptoms had disappeared. These results suggest that KMT can be an effective method to treat metastatic bladder cancer in the lungs.
Case Rep Oncol. 2014 May;7(2):534-40.
PMID: 25232323 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
|
| 12. |
The use of an anti-inflammatory supplement in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Moreillon JJ, Bowden RG, Deike E, Griggs J, Wilson R, Shelmadine B, Cooke M, Beaujean A
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is characterized by a continuous reduction in kidney function, increased inflammation, and reduced antioxidant capacity. The objective of this study was to assess the effects of a herbal supplement on systemic inflammation and antioxidant status in non-dialysis CKD patients. Sixteen patients with CKD (56.0±16.0 yrs, 171.4±11.9 cm, 99.3±20.2 kg) were randomly chosen to receive a herbal supplement composed of Curcuma longa and Boswellia serrata, or placebo. Plasma levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and serum C-reactive protein (CRP) were measured at baseline and 8 weeks. Baseline data demonstrated elevated inflammation and low antioxidant levels. A significant time effect (p=0.03) and time x compliance interaction effect (p=0.04) were observed for IL-6. No significant differences were observed for any other variables. This study demonstrates that mild and moderate CKD is associated with chronic inflammation and low antioxidant activity. Systemic inflammation and impaired antioxidant status may be greater in CKD populations with multiple comorbidities. Curcumin and Boswellia serrata are safe and tolerable and helped to improve the levels of an inflammatory cytokine.
J Complement Integr Med. 2013 Jul;10():.
PMID: 23828329 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 13. |
Boswellia serrata acts on cerebral edema in patients irradiated for brain tumors: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind pilot trial.
Kirste S, Treier M, Wehrle SJ, Becker G, Abdel-Tawab M, Gerbeth K, Hug MJ, Lubrich B, Grosu AL, Momm F
BACKGROUND: Patients irradiated for brain tumors often suffer from cerebral edema and are usually treated with dexamethasone, which has various side effects. To investigate the activity of Boswellia serrata (BS) in radiotherapy-related edema, we conducted a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, pilot trial.
METHODS: Forty-four patients with primary or secondary malignant cerebral tumors were randomly assigned to radiotherapy plus either BS 4200 mg/day or placebo. The volume of cerebral edema in the T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequence was analyzed as a primary endpoint. Secondary endpoints were toxicity, cognitive function, quality of life, and the need for antiedematous (dexamethasone) medication. Blood samples were taken to analyze the serum concentration of boswellic acids (AKBA and KBA).
RESULTS: Compared with baseline and if measured immediately after the end of radiotherapy and BS/placebo treatment, a reduction of cerebral edema of >75% was found in 60% of patients receiving BS and in 26% of patients receiving placebo (P = .023). These findings may be based on an additional antitumor effect. There were no severe adverse events in either group. In the BS group, 6 patients reported minor gastrointestinal discomfort. BS did not have a significant impact on quality of life or cognitive function. The dexamethasone dose during radiotherapy in both groups was not statistically different. Boswellic acids could be detected in patients' serum.
CONCLUSIONS: BS significantly reduced cerebral edema measured by MRI in the study population. BS could potentially be steroid-sparing for patients receiving brain irradiation. Our findings will need to be further validated in larger studies.
Cancer. 2011 Aug;117(16):3788-95.
PMID: 21287538 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 14. |
Temporary anti-cancer & anti-pain effects of mechanical stimulation of any one of 3 front teeth (1st incisor, 2nd incisor, & canine) of right & left side of upper & lower jaws and their possible mechanism, & relatively long term disappearance of pain & cancer parameters by one optimal dose of DHEA, Astragalus, Boswellia Serrata, often with press needle stimulation of True ST. 36.
Omura Y, Horiuchi N, Jones MK, Lu DP, Shimotsuura Y, Duvvi H, Pallos A, Ohki M, Suetsugu A
One minute downward pressure on the tip of any one of the front 3 teeth (1st incisor, 2nd incisor, and canine) at the right and left sides of the upper and lower jaw by a wooden toothpick induced temporary disappearance (20 min approximately 4 hours) of abnormally increased pain parameters (pain grading, Substance P, & TXB2), and cancer parameters (Telomere, Integrin alpha5beta1, Oncogene C-fos Ab2, etc. of Astrocytoma, Glioblastoma, squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus, adenocarcinoma of lung, breast cancer, adenocarcinoma of colon, prostate cancer). The effect included temporary disappearance of headache, toothache, chest and abdominal pain, and backache, often with improved memory & concentration. Since these beneficial changes resembled the effects of giving one optimal dose of DHEA, increase of DHEA was measured. Above mechanical stimulation of one of these front teeth increased abnormally reduced DHEA levels of less than 10 ng to norm1 100 approximately 130 ng BDORT units and normal cell (NC) telomeres from markedly reduced values to near normal values, and improved acetylcholine in the Hippocampus. Large organ representation areas for the Adrenal gland & Hippocampus may exist at these front teeth. This method can be used for emergency pain control and can explain the beneficial effect of bruxism and tooth brushing, through the increase of DHEA levels and activities of the Hippocampus by increasing Acetylcholine. Increasing NC telomere to optimally high level resulted in disappearance of pain and improvement or significant reduction of malignant tumor. Repeated daily press needle stimulation of True ST. 36 increased NC telomere 450-700 ng BDORT units. One optimal dose of DHEA increased NC telomere 525 ng DBORT units and eliminated the pain and abnormally increased cancer parameters; effect of one optimal dose lasted 0.5-11 months. One optimal dose of Boswellia Serrata or Astragalus not only increased NC telomere 650 ng BDORT units, eliminating pain and cancer parameters, but also reduced the size of the Astrocytoma grade I by 10-20% and the Glioblastoma by 15-90% in less than 2-6 months in some patients, as long as high NC telomere is maintained.
Acupunct Electrother Res. 2009;34(3-4):175-203.
PMID: 20344885 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 15. |
[Effects of aroma hand massage on pain, state anxiety and depression in hospice patients with terminal cancer].
Chang SY
PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of aroma hand massage on pain, state anxiety and depression in hospice patients with terminal cancer.
METHODS: This study was a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design. The subjects were 58 hospice patients with terminal cancer who were hospitalized. Twenty eight hospice patients with terminal cancer were assigned to the experimental group (aroma hand massage), and 30 hospice patients with terminal cancer were assigned to the control group (general oil hand massage). As for the experimental treatment, the experimental group went through aroma hand massage on each hand for 5 min for 7 days with blended oil-a mixture of Bergamot, Lavender, and Frankincense in the ratio of 1:1:1, which was diluted 1.5% with sweet almond carrier oil 50 ml. The control group went through general oil hand massage by only sweet almond carrier oil-on each hand for 5 min for 7 days.
RESULTS: The aroma hand massage experimental group showed more significant differences in the changes of pain score (t=-3.52, p=.001) and depression (t=-8.99, p=.000) than the control group.
CONCLUSION: Aroma hand massage had a positive effect on pain and depression in hospice patients with terminal cancer.
Taehan Kanho Hakhoe Chi. 2008 Aug;38(4):493-502.
PMID: 18753801 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 16. |
A lipoxygenase inhibitor in breast cancer brain metastases.
Flavin DF
The complication of multiple brain metastases in breast cancer patients is a life threatening condition with limited success following standard therapies. The arachidonate lipoxygenase pathway appears to play a role in brain tumor growth as well as inhibition of apoptosis in in-vitro studies. The down regulation of these arachidonate lipoxygenase growth stimulating products therefore appeared to be a worthwhile consideration for testing in brain metastases not responding to standard therapy. Boswellia serrata, a lipoxygenase inhibitor was applied for this inhibition. Multiple brain metastases were successfully reversed using this method in a breast cancer patient who had not shown improvement after standard therapy. The results suggest a potential new area of therapy for breast cancer patients with brain metastases that may be useful as an adjuvant to our standard therapy.
J Neurooncol. 2007 Mar;82(1):91-3.
PMID: 17001517 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 17. |
Response of radiochemotherapy-associated cerebral edema to a phytotherapeutic agent, H15.
Streffer JR, Bitzer M, Schabet M, Dichgans J, Weller M
Twelve patients with brain tumors and progressive edema caused by tumor progression or radiochemotherapy-related leukoencephalopathy were treated with H15, a phytotherapeutic anti-inflammatory agent. Edema was reduced in two of seven patients with glioblastoma with tumor progression and in three of five patients with treatment-related leukoencephalopathy. All patients with leukoencephalopathy improved clinically for several months.
Neurology. 2001 May;56(9):1219-21.
PMID: 11342692 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|
| 18. |
Boswellic acids in the palliative therapy of children with progressive or relapsed brain tumors.
Janssen G, Bode U, Breu H, Dohrn B, Engelbrecht V, Göbel U
19 children and adolescents with intracranial tumors received a palliative therapy with H 15 at a maximum dose of 126 mg/kg BW/day. All patients had previously been treated with conventional therapy. No side effects were observed during a median 9 months application. The recently reported antiedematous effect of H 15 was documented by MRI in one patient with a peritumoral edema, thus sparing steroid therapy with its typical side effects. Five/19 children reported an improvement of their general health status; this might be a psychological effect of hope for tumor response during palliative care. Three/17 patients with malignant tumors showed a mainly transient improvement of neurological symptoms such as pareses and ataxia. Three further patients showed an increased muscular strength and one cachectic patient achieved a weight gain. These improvements might be attributed to the antiedematous effect of H 15. Because of the palliative situation of these patients, H 15 application was performed without prior rebiopsy for histological evaluation. Overlapping effects with a previous radiotherapy or chemotherapy may have occurred. An antiproliferative effect cannot be stated. To prevent an uncritical use of H 15, further studies with prospective central documentation have to be initiated to evaluate the clinical indications for H 15 in palliative therapy, optimal dosage and duration of application.
Klin Padiatr. 2000 Jul-Aug;212(4):189-95.
PMID: 10994549 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
|